
Let's be real, most companies today are sitting on a mountain of data. You've got customer interactions, sales figures, website clicks, support tickets... it's a lot. The hard part isn't just collecting all that info; it's making sense of it without waiting forever or spending a fortune.
That’s exactly the problem Amazon Redshift was built to solve. It’s a cloud data warehouse designed to chew through massive amounts of data for analytics. This post is a complete Redshift overview for 2025. We'll get into its architecture, what it’s good at, how the pricing works, and its limitations so you can decide if it’s the right fit for you.
What is Amazon Redshift?
So, what is Amazon Redshift, really? It's AWS's take on a massive, cloud-based data warehouse. Think of a database that's been built specifically for one job: analyzing huge datasets (what the pros call Online Analytical Processing, or OLAP). It’s perfect for running the complex queries you need for business intelligence, reporting, and digging into your data.
While its roots are in PostgreSQL, Redshift has been heavily tweaked for analytical speed. It’s not designed for the quick, everyday transactions your main application database handles, like processing a single customer order. Instead, its whole purpose is to give you fast, scalable analytics on big data, for way less than what you’d pay for a traditional on-premise setup.
Redshift's core architecture
Redshift's speed isn't magic; it comes down to a clever architecture designed for parallel processing. Let's pull back the curtain and see how it works.
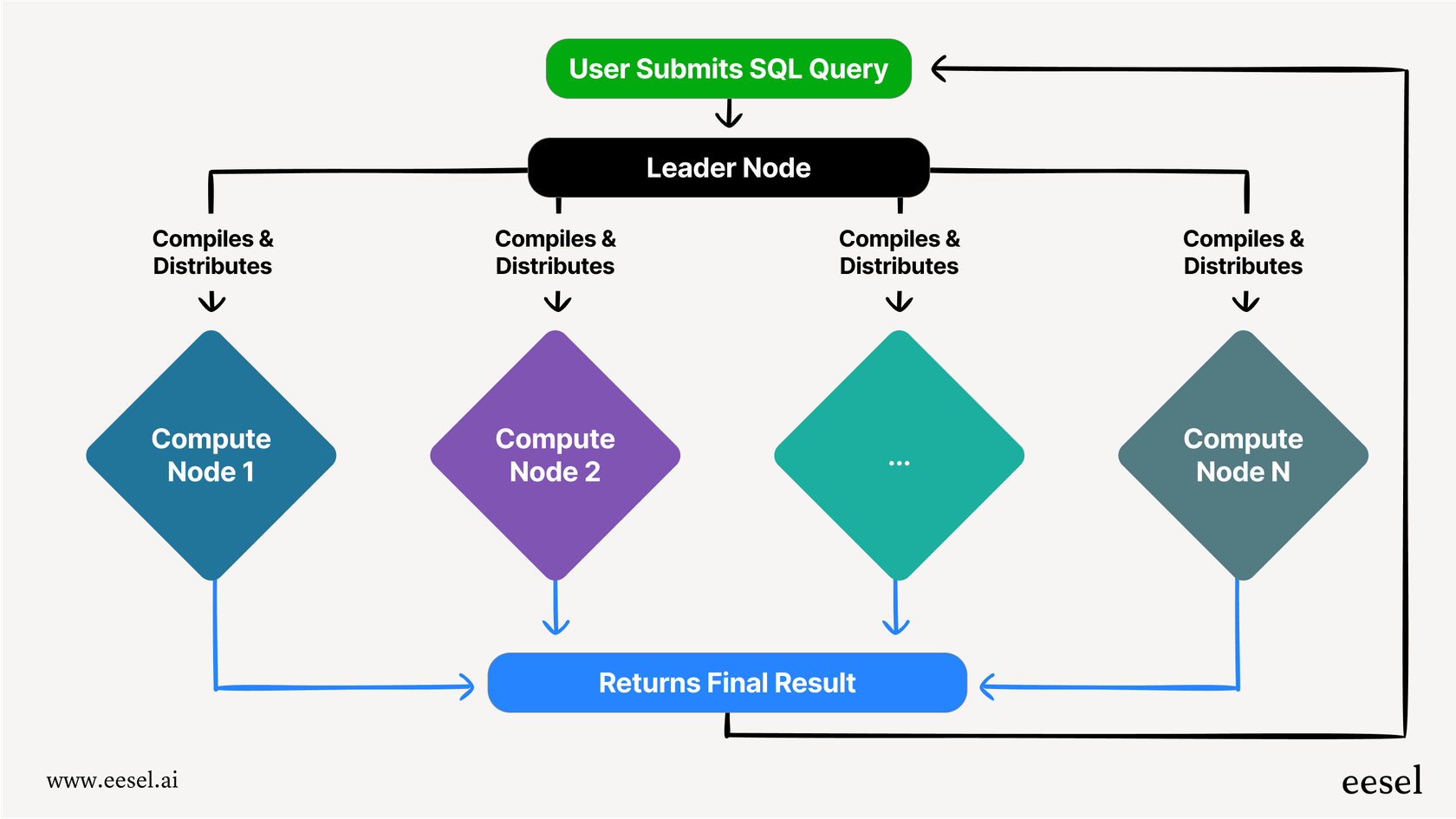
The leader node and compute nodes
Every Redshift setup, or "cluster," has two main parts. First, there's the leader node. You can think of it as the project manager. When your application sends a query, the leader node receives it, figures out the best plan to execute it, and then delegates the work to a team of compute nodes.
The compute nodes are the ones that do the heavy lifting. They’re the workers that store your data and actually run the pieces of the query they’re assigned. Once they finish their part, they send the results back to the leader node, which pieces everything together and hands you the final answer.
Massively parallel processing (MPP)
The secret sauce that makes Redshift so fast is something called Massively Parallel Processing (MPP). Instead of trying to solve a giant, complicated query with one powerful machine, MPP chops it up into smaller, more manageable pieces. These pieces are then run at the same time (in parallel) across all the different compute nodes.
Think of it like trying to count a massive pile of ballots. One person doing it alone would be there all year. But if you give a small stack to a hundred different people, they can all count their pile at the same time and finish way faster. That's the core idea behind how Redshift tackles your queries.
Columnar storage
Most databases you're used to probably use row-based storage. This means all the information for a single record (like one customer's name, address, and purchase history) is stored together in a row. Redshift flips this on its head and uses columnar storage, which groups all the data from a single column together.
This might sound like a small technical detail, but it makes a huge difference for analytics. When you're running a report, you usually only care about a few columns, not every single piece of data in a table. For example, maybe you just want to find the total sum of sales from a huge transactions table that has 50 different columns. With columnar storage, Redshift only needs to read the data in the single "sales" column, completely ignoring the other 49. This massively cuts down on the amount of data it has to scan, which makes your queries run a whole lot faster.
Key features and common use cases
Now that you have a sense of the "how," let's talk about the "what." What do people actually use Redshift for?
Business intelligence and reporting
This is Redshift's primary job. It acts as the powerful engine behind business intelligence (BI) tools like Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, and Amazon QuickSight. Companies connect these tools to Redshift to build dashboards that let them track just about anything, from daily sales numbers and marketing campaign performance to factory floor efficiency.
Real-time analytics on large datasets
Redshift is also beefy enough to handle and analyze streams of data as they come in. By connecting it to services like Amazon Kinesis, companies can power things like live fraud detection systems, real-time leaderboards for video games, or dashboards that analyze data pouring in from IoT sensors.
Aggregating multiple data sources
One of the coolest things Redshift can do is pull together data from different systems. It has a feature called Redshift Spectrum that lets you run queries on data sitting in your regular databases and on semi-structured files (like JSON) that are just sitting in a data lake in Amazon S3.
For instance, a business could combine support ticket data from a platform like Zendesk, sales data from their CRM, and product usage data from their app logs. By bringing all of that into Redshift, they can finally get a single, complete picture of a customer's entire journey.
Amazon Redshift pricing in 2025
Nobody likes a surprise bill, so picking the right pricing model for Redshift is pretty important. AWS gives you two main ways to pay, and each is better for different situations.
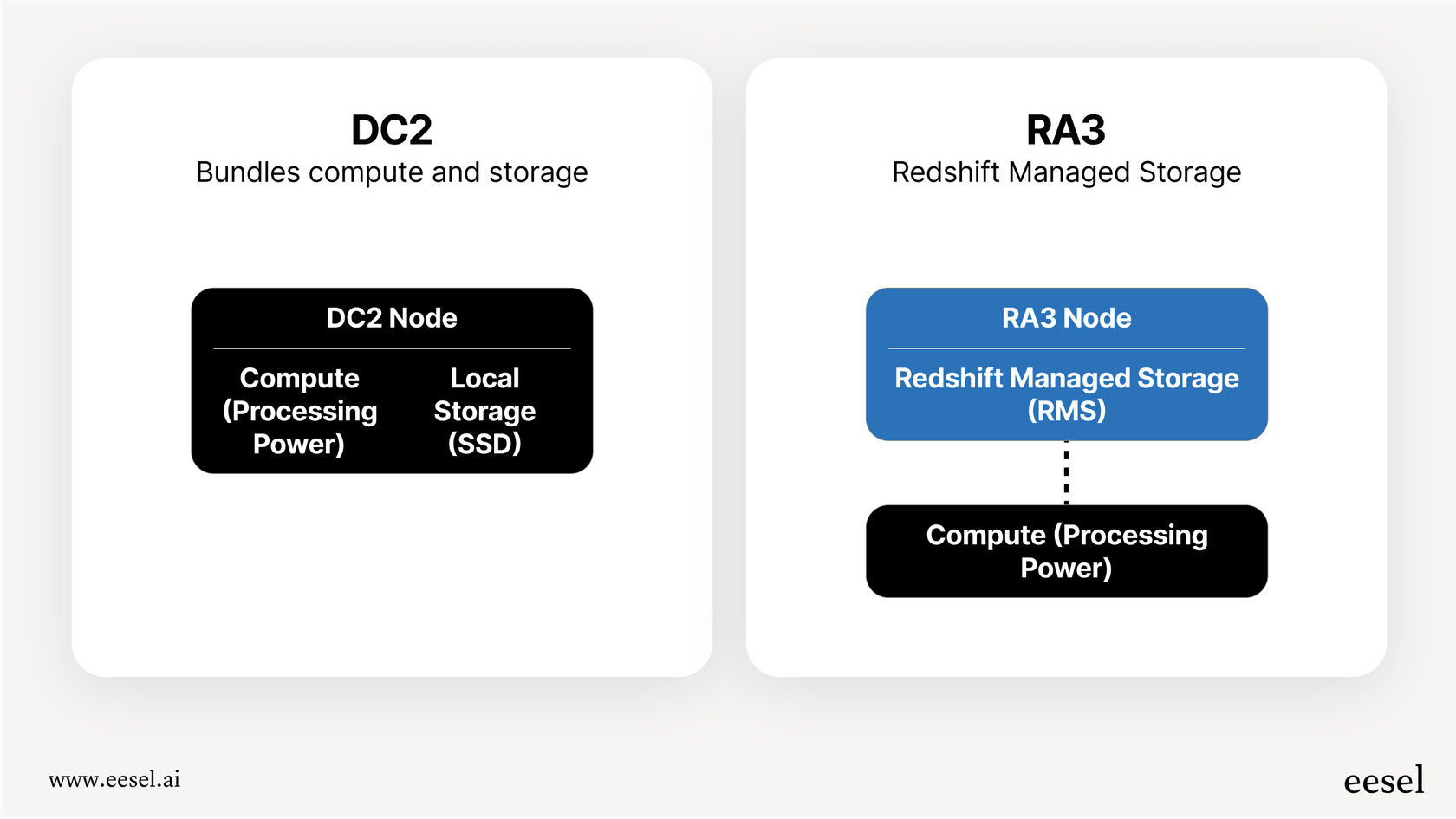
Provisioned clusters
This is the classic approach. You choose the specific type and number of servers (which AWS calls nodes) you want, and you pay for them by the hour. The most common option these days is the RA3 node type, which cleverly splits compute power from storage. This means you can scale up your processing power without having to pay for more storage, and vice versa. This model works well if your workload is steady and predictable. If you know you'll need it for a while, you can also get big discounts by committing to a one or three-year term with Reserved Instances.
Redshift serverless
This is the newer, more hands-off option. With Redshift Serverless, you don't have to think about clusters or nodes at all. AWS manages everything behind the scenes, automatically spinning up resources when you need them and shutting them down when you don't. You only pay for the compute time you actually use, measured in Redshift Processing Units (RPUs) per hour. This is a great choice for workloads that are spiky, unpredictable, or just don't run 24/7.
Pricing comparison table
Here’s a quick comparison to help you see the difference. For the latest numbers, you should always check the official AWS Redshift pricing page.
| Feature | Provisioned Clusters | Redshift Serverless |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Model | Pay per hour for nodes (e.g., $0.543/hour and up) | Pay per RPU-hour for compute used (e.g., $1.50/hour and up) |
| Best For | Stable, predictable, and high-volume workloads | Variable, unpredictable, or intermittent workloads |
| Management | You need to plan capacity and manage the cluster | Zero administration, AWS handles it all |
| Scaling | Manual or scheduled scaling (can cause brief downtime) | Scales up and down automatically and seamlessly |
Just remember there can be other costs, like fees for managed storage or for using Redshift Spectrum to query data in S3.
Strengths and limitations of Redshift
Like any technology, Redshift is great at some things and not so great at others. It's good to know both sides of the story before you jump in.
Pros: Key benefits
-
Speed at Scale: Its core design lets it run queries on huge datasets incredibly fast.
-
Cost-Effective: It's generally much cheaper than buying and managing your own data warehouse hardware.
-
Deep AWS Integration: It plays nicely with the whole suite of AWS services, like S3 for storage, Glue for data prep, and Kinesis for streaming data.
-
Scalability: You can start small and grow your warehouse to petabytes of data as your company grows.
Cons: Common pitfalls and limitations
-
It's for analysis, not for transactions: Redshift is designed for big, complex queries. It's actually quite slow at handling lots of small updates, inserts, or deletes.
-
There's a learning curve: The 'provisioned' version isn't exactly plug-and-play. To get your money's worth, you'll need to get familiar with terms like 'distribution keys' and 'sort keys' and know when to do a little maintenance.
-
Costs can creep up: If you're not careful, inefficient queries or a poorly configured cluster on a pay-as-you-go model can lead to a bigger bill than you expected.
-
Vendor Lock-in: Since it's a native AWS service, moving all your data and processes to a different cloud provider later on could be a big, expensive headache.
From data insights to automated action
Redshift is an amazing tool for analysis. It helps you spot trends and find insights buried in your data. For example, after looking at a million support tickets, you might discover that a quarter of all customer questions are about your return policy.
Okay, so you've found this great insight. What now? Usually, this kicks off a bunch of manual work. Someone has to update the knowledge base, write new saved replies for the support team, and maybe even organize a training session. It's slow, and you're always playing catch-up. This is where you need something that can act on your findings.
This is where an AI support agent comes in. A tool like eesel AI can connect directly to your helpdesk and all your knowledge sources. You can train it on the same support tickets you analyzed in Redshift, so it understands your business, your brand voice, and the right answers to common questions right away. Instead of just writing a report that says "people ask about returns a lot," you can build an AI agent that just handles those questions instantly.
With eesel AI, this isn't some six-month project. It's a self-serve platform that lets you go live in minutes. You can even run a simulation on your past tickets to see exactly how many issues it could have resolved automatically, giving you a clear picture of its impact before you even turn it on for customers.
Final thoughts
Amazon Redshift is a seriously powerful data warehouse that can help you unlock insights from huge datasets, whether you're building BI dashboards or doing deep-dive analytics. You can choose a Provisioned cluster for its predictable costs or go with the Serverless option for its amazing flexibility.
But finding an insight is only half the job. The real magic happens when you connect that analysis to an action. Automating the response to the patterns you uncover is how you build a truly efficient, data-driven company.
Ready to turn your support data from insights into automated action? Try eesel AI for free and see how quickly you can start automating your customer support.
Frequently asked questions
Amazon Redshift is a cloud-based data warehouse optimized for online analytical processing (OLAP) on massive datasets. It's built to handle complex queries for business intelligence, reporting, and deep data analysis, differing significantly from transactional databases.
Redshift achieves speed through Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) across leader and compute nodes, and by using columnar storage. MPP breaks queries into smaller parts executed simultaneously, while columnar storage efficiently reduces the data scanned for analytics.
Redshift excels in business intelligence and reporting, powering dashboards and analytics tools. It's also effectively used for real-time analytics on large data streams and for aggregating data from various sources into a single comprehensive view.
Redshift offers provisioned clusters, where you pay hourly for fixed resources, ideal for stable workloads, and serverless, where you pay per compute-hour for automatically scaled resources, which is perfect for variable or unpredictable tasks.
Strengths include speed at scale, cost-effectiveness, and deep AWS integration. Limitations involve its unsuitability for transactional workloads, a learning curve for optimal configuration, potential cost creep, and vendor lock-in.
While the provisioned version requires understanding concepts like distribution and sort keys for optimal performance, Redshift Serverless significantly reduces administrative overhead. This makes it much easier for new users to get started without needing deep technical expertise.
Share this post

Article by
Stevia Putri
Stevia Putri is a marketing generalist at eesel AI, where she helps turn powerful AI tools into stories that resonate. She’s driven by curiosity, clarity, and the human side of technology.







