By building its own browser, OpenAI isn't just making a new app; it's creating a direct pipeline to user data. This is exactly how Google has maintained its dominance for two decades. Having access to real-time user behavior, browsing history, and preferences is the fuel needed to train smarter AI agents that can start to anticipate what you need.
Of course, this brings up some big questions about privacy. As publications like ZDNET have pointed out, how this data is handled will be a make-or-break factor for many people. OpenAI has mentioned safeguards, like a "takeover mode" for sensitive information like passwords and credit card details, but the trend is clear: the more an agent knows about you, the more it can do for you.
The OpenAI browser for personal use vs. AI agents for business support
The OpenAI browser is shaping up to be a fantastic tool for individual productivity. But when you’re talking about business functions like customer support, a general-purpose agent made for consumers just isn't going to cut it. Professional environments need specialized AI agents that have deep integrations, custom training on company knowledge, and strong controls that a generic browser can't offer.
Let's look at three key limitations of using a consumer-grade AI agent for business, and how a purpose-built platform is designed to handle them.
Limitation 1: No deep integration with business systems
The OpenAI browser works by navigating the public parts of websites. It can’t connect to your internal help desk, check an order status in your private database, or pull up a customer's history from your CRM. It’s like hiring a new employee who only has access to your public website and nothing else.
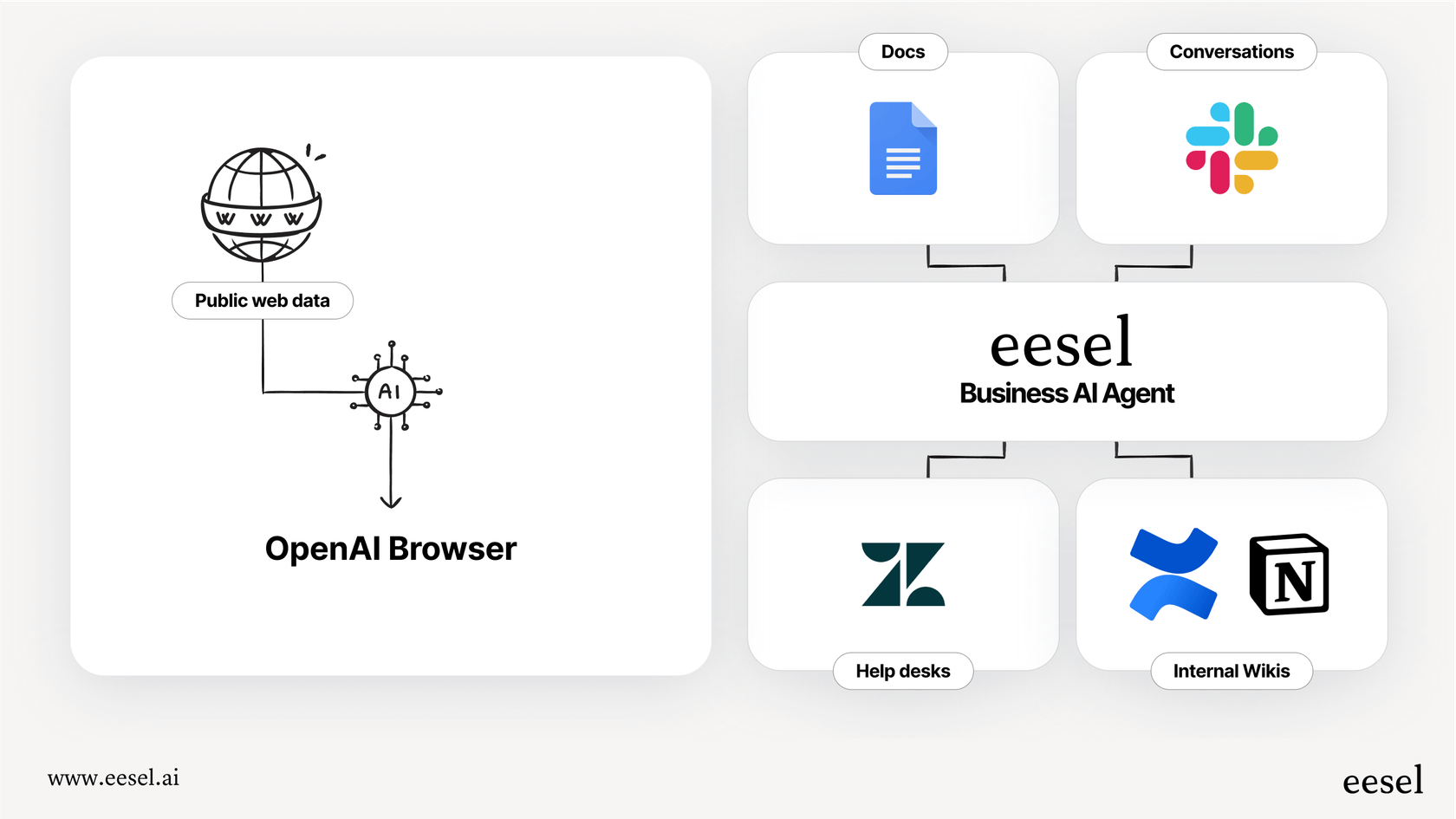
This is where a dedicated platform like eesel AI comes in. It doesn't justscrape screens; it uses one-click integrations to connect directly to the tools your business already uses. This lets its AI support agent perform real, useful actions, like tagging tickets in Zendesk, escalating issues to the right team in Jira Service Management, or pinging your Shopify API to get live order information for a customer.
Limitation 2: Trained on the public web, not your expert knowledge
An agent trained on the entire internet doesn't know your company's specific return policy, the technical details of your latest software update, or the solutions hiding in thousands of your past support tickets. Its answers will be generic if you're lucky, and flat-out wrong if you're not.
That’s why eesel AI trains securely on your internal business knowledge. It connects to your past support tickets, internal guides in Confluence and Google Docs, and your public help center articles. This makes sure the answers it gives are accurate, on-brand, and based on your team's hard-won expertise, not just a summary of a Wikipedia page.
Limitation 3: No business logic or safety controls
You can't really program a general browser agent with specific business rules like, "Always escalate tickets from VIP customers to a senior agent," or "If a user mentions 'refund' three times, automatically open a ticket for a manager." You’re pretty much stuck with whatever features it comes with.
A platform like eesel AI puts you in the driver's seat. With "human-in-the-loop" features, you can set up precise escalation rules using plain English, define a specific tone of voice for the AI, and even run simulations on past tickets to check its accuracy before it ever talks to a customer. This gives you the reliability and safety net that professional support teams really need.
| Feature | OpenAI Browser (for Personal Use) | eesel AI (for Business Support) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Automate individual web tasks | Automate and assist customer support workflows |
| Integrations | Interacts with public web UI | One-click with Zendesk, Slack, Shopify, etc. |
| Training Data | General public internet | Your private tickets, docs, & help center |
| Control & Rules | Limited to user prompts | Granular, natural language guardrails & escalation |
| Business Actions | Clicks, types, scrolls on websites | Tags tickets, makes API calls, routes issues |
| Analytics | None for business use | In-depth reporting on performance & knowledge gaps |
What's next for the OpenAI browser, AI, and the web?
OpenAI isn't the only one in this race. Competitors like Perplexity with its Comet browser, Microsoft with Copilot baked into Edge, and Google with Gemini in Chrome are all pushing toward a future where the browser is an active partner in our digital lives.
OpenAI unveils a ChatGPT-powered browser that lets you navigate, book, and summarize the web through conversation.
We're watching the internet change from a collection of places we visit into a huge, connected database that AI agents can use to get things done for us. For businesses, this means the edge will no longer come from having the slickest website, but from having the smartest and most helpful AI agents serving your customers.
Your personal agent is coming, but your business agent is already here
The OpenAI browser is a clear sign that an exciting, AI-first internet is on its way, and it’s going to make us all more productive. It’s a huge step forward.
But for businesses dealing with important tasks like customer service, a generic tool just isn't enough. You need specialized, integrated, and controllable AI agents built for the messy reality of your operations. The future is about using the right AI for the right job, whether that’s helping one person book a flight or helping a global team resolve thousands of customer issues.
The OpenAI browser can manage your personal tasks, but what about your business?
You can deploy an AI agent built to handle customer support with the control and integrations your business needs. eesel AI plugs into your existing help desk and knowledge sources in minutes to automate frontline support, draft replies for your team, and improve customer satisfaction.
Start your free trial or book a demo and build your first business-ready AI agent today.
Frequently asked questions
The key difference is action versus information. A ChatGPT extension can summarize or answer questions about a page, but the OpenAI browser is designed to take multi-step actions on your behalf, like booking an appointment or ordering a product across different pages.
Yes, most likely. Reports indicate the browser is built on Chromium, the same open-source project that powers Google Chrome. This means it should be compatible with the vast majority of existing Chrome extensions right from the start.
OpenAI has acknowledged this is a major concern. They have mentioned building in safeguards, like a "takeover mode" where the AI agent hands control back to you for entering sensitive data like passwords or payment details to ensure they remain secure.
You certainly could for simple, public-facing tasks like looking up information or booking a public reservation. However, it lacks the deep integrations with internal business systems (like your CRM or help desk) and the security controls needed for more complex company workflows.
While both aim to integrate AI into browsing, OpenAI's approach seems more focused on autonomous agents that complete complex goals you set. Copilot is currently more of an embedded assistant that helps with tasks on your current page, like summarizing text or drafting emails.
A chatbot responds with information, but an agent takes action. Instead of telling you how to book a flight, the agent in the OpenAI browser can actually go through the steps of searching, selecting, and filling out the forms for you, turning your instruction into a completed task.
Share this post

Article by
Stevia Putri
Stevia Putri is a marketing generalist at eesel AI, where she helps turn powerful AI tools into stories that resonate. She’s driven by curiosity, clarity, and the human side of technology.







