
Remember when talking to your devices felt like something out of a sci-fi movie? Well, it's not sci-fi anymore. We ask our phones for directions, chat with smart speakers, and even get help from automated voice systems when we call the bank.
This shift means businesses are starting to realize that clunky, text-only chatbots just don't always cut it. People want to talk. And for companies looking to build these more natural, voice-based experiences, the OpenAI Audio API is often the first tool they reach for.
It gives developers the building blocks to create everything from simple narration tools to complex, real-time voice agents. But turning those blocks into a reliable business solution is a whole other story.
This guide will walk you through what the OpenAI Audio API is, what it can do, and how people are using it. We'll also get real about the practical side of things, like how much it costs and the technical headaches involved, so you can figure out if building a custom voice solution is the right move for you.
What is the OpenAI Audio API?
First things first, the "OpenAI Audio API" isn't a single product. It’s more like a collection of different models and tools that all work with sound. Think of it as a toolkit for anything voice-related.
Its main talents fall into three buckets:
-
Speech-to-text: Taking what someone says and turning it into written text.
-
Text-to-speech: Reading written text out loud in a natural-sounding voice.
-
Speech-to-speech: Powering real-time voice conversations that feel smooth and natural.
Each of these jobs is handled by different models. For speech-to-text, you’ve got options like "whisper-1" and the newer "gpt-4o-transcribe". For text-to-speech, you'd use models like "tts-1" and "gpt-4o-mini-tts". And for those live conversations, there's a specialized model called "gpt-realtime".
While these tools are seriously impressive, they're still just tools. Getting them to work smoothly within your business, connecting them to your customer data, and making them dependable enough for real-world use takes a fair bit of development work.
A look under the hood: OpenAI Audio API models and features
Building a full voice experience isn't as simple as making one API call. You usually have to stitch together different pieces, each with its own model and function. Let's break down the main components.
From speech to text
Before you can respond to someone, you have to understand what they said. That's where OpenAI's "transcriptions" endpoint comes in, powered by models like "gpt-4o-transcribe" and the well-known "whisper-1".
It’s known for being incredibly accurate across dozens of languages, but the cool part is in the details. You can give it prompts to help it recognize specific or unusual words and acronyms, which is a huge help for businesses with unique product names. With "whisper-1", you can even get timestamps for each word or sentence, which is perfect for creating subtitles or analyzing call recordings.
One practical thing to keep in mind is the file size limit. The API only takes files up to 25 MB. So if you're working with long recordings like hour-long meetings or extended support calls, you'll need to build a way to chop them into smaller pieces first.
From text to speech
Once your app understands the user, it needs a voice to reply. The "speech" endpoint handles this, with the new "gpt-4o-mini-tts" model being the star of the show.
What makes this model interesting is its ability to follow "instructions" on how to speak. You can tell it to "speak cheerfully" or "use a sympathetic tone," giving you more creative control over the user's experience. There's a whole cast of built-in voices to pick from, like "alloy", "onyx", and "nova". If you're curious, you can listen to them over at OpenAI.fm.
The API also supports different audio formats. MP3 is the default, but you can choose something like PCM or WAV if you're building a real-time app and need to cut down on any delay from decoding the audio.
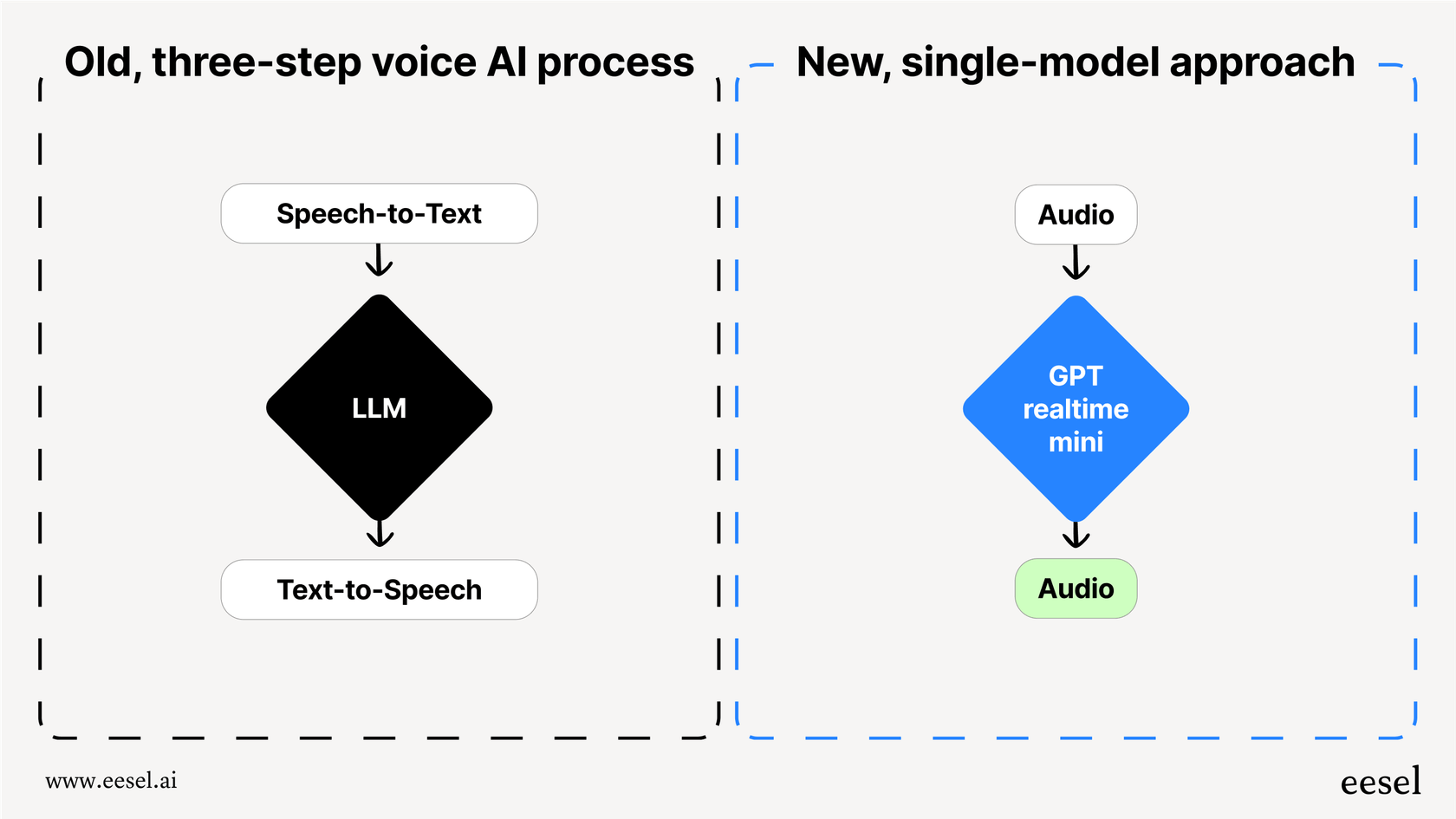
Real-time chats with the gpt-realtime model
For conversations that feel as natural as talking to a person, OpenAI has the Realtime API. Instead of the old-school method of chaining together separate speech-to-text, language model, and text-to-speech calls (which adds a noticeable lag), the "gpt-realtime" model processes audio directly.
This all-in-one approach cuts down the delay quite a bit, making it possible to have fluid conversations where the AI can be interrupted, just like a person. It’s the closest you can get to building something like ChatGPT's Advanced Voice Mode. The API even supports SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), so you can hook your voice agent right into your phone systems.
But all that power comes with more complexity. Using the Realtime API means you’re managing WebSocket connections and wiring up all the logic yourself. It's a fantastic tool, but it's definitely for developers who are ready to roll up their sleeves.
What can you actually build with the OpenAI Audio API?
With these tools at your disposal, you can create a whole range of voice-powered apps. Here are a few of the most popular ideas.
Building voice agents for customer support
The biggest use case for businesses is creating AI voice agents for call centers. An agent can listen to a caller's problem, figure out what they need, search a knowledge base for the answer, and reply in a helpful, natural-sounding voice. This can take care of common questions, letting your human agents focus on trickier issues.
But here’s the catch: building a production-ready voice agent from scratch is a huge project. You have to manage the audio streams in real time, connect to your helpdesk, and train the AI on your company’s specific support topics. This is exactly why many teams opt for a platform that handles the heavy lifting. For example, eesel AI offers an "AI Agent" that plugs directly into helpdesks like Zendesk and Freshdesk. Instead of spending months coding, you can launch a voice-capable agent that learns from your existing support tickets and help docs in just a few minutes.

Real-time transcription and translation
Beyond customer support, the APIs are great for transcribing meetings, lectures, and interviews. The timestamp feature in "whisper-1" is really handy for creating accurate subtitles for videos or syncing a written transcript with an audio file. You can also use the "translations" endpoint to instantly translate spoken words from one language into English.
Creating more accessible content
Text-to-speech is also a fantastic tool for making content more accessible. You can use the API to narrate blog posts, articles, or even books, opening up your content to people with visual impairments or anyone who just prefers to listen. It can also be used to add audio descriptions to apps, making the experience better for everyone.
The tricky part: Pricing and technical hurdles
While the possibilities are exciting, there are some real-world costs and challenges you need to think about before jumping in. This is where a lot of teams get stuck.
Understanding the costs
The pricing for the OpenAI Audio API, especially for real-time conversations, can be a major roadblock.
Let's talk numbers. The "gpt-realtime" model, which handles those fluid back-and-forth conversations, is priced based on "audio tokens." You're charged for what it hears (input) and what it says (output). The input costs around $100 per million audio tokens, which works out to roughly $0.06 per minute. The output is more than double that, at $200 per million tokens, or about $0.24 per minute.
When you add it all up, a simple two-way conversation can get expensive fast. A single hour-long support call could run you around $18 ($0.30/min * 60 min), and that doesn't even count any extra text processing costs. For a busy call center, these expenses can become a budgeting nightmare.
| Feature | Price (per 1M audio tokens) | Price (per minute, approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Input Audio | $100 | $0.06 |
| Output Audio | $200 | $0.24 |
| Total (Two-way) | - | $0.30 |
Navigating technical challenges
On top of the cost, there are technical obstacles. As we mentioned earlier, you'll need to build a system for chopping up audio files larger than 25MB, manage ongoing WebSocket connections for real-time audio, and write all the code to connect the different API calls if you're not using the "gpt-realtime" model. This all demands specialized engineering skills and a lot of development time.
The alternative: Using an integrated platform
This brings us to the classic "build vs. buy" debate. Instead of wrestling with these problems yourself, you can use a platform that has already figured them out.
eesel AI was built to be the fastest and most straightforward way to deploy a voice AI agent. It tackles the big problems of cost and complexity directly. With clear, predictable pricing based on a set number of monthly interactions, you won't get a shocking bill after a busy month. No confusing token math or hidden fees.
Even better, eesel AI gets rid of the development headache.
-
Go live in minutes, not months: With one-click connections to your existing helpdesk and knowledge sources, you don't need to write any code.
-
Test with confidence: A powerful simulation mode lets you test your AI on thousands of your past support tickets. This way, you can see exactly how it will perform and calculate your potential return on investment before you launch.
-
Bring all your knowledge together: Connect your AI to all your existing documentation, whether it lives in Confluence, Google Docs, or your past support tickets, to make sure it gives accurate and relevant answers from day one.

Should you build or buy a voice AI solution?
The OpenAI Audio API offers an incredible set of tools for creating the next generation of voice experiences. The technology is flexible, powerful, and has the potential to completely change how businesses talk to their customers.
But turning those tools into a solution that is reliable, scalable, and affordable is a massive project. It requires serious technical know-how, a big investment of time and money, and a stomach for unpredictable costs.
For most businesses, the choice becomes pretty clear: do you want to spend months building a custom voice solution from the ground up, or do you want to launch a ready-to-go AI agent in a fraction of the time with costs you can actually predict?
Ready to deploy a powerful voice agent without the development grind and surprise bills? Start your free eesel AI trial and see just how easy it is to automate support right inside your existing helpdesk.
Frequently asked questions
The OpenAI Audio API offers three main capabilities: speech-to-text (e.g., "whisper-1", "gpt-4o-transcribe"), text-to-speech (e.g., "tts-1", "gpt-4o-mini-tts"), and real-time speech-to-speech conversations ("gpt-realtime"). It essentially provides a comprehensive toolkit for voice interactions.
The "gpt-realtime" model charges for both input and output audio tokens, costing roughly $0.06 per minute for input and $0.24 per minute for output. A single hour-long, two-way conversation could sum up to about $18, making costs difficult to predict for high-volume use.
Developers often face challenges like managing audio files larger than 25MB by splitting them, handling persistent WebSocket connections for real-time interactions, and coding the intricate logic to connect various API calls. These tasks require specialized engineering skills and significant development time.
The "gpt-realtime" model enables fluid, interruptible conversations by processing audio directly, significantly reducing latency compared to chaining separate API calls. This allows for experiences akin to ChatGPT's Advanced Voice Mode, including SIP support for phone systems.
Yes, the API has a 25 MB file size limit for audio uploads for transcription. If you're working with longer recordings, you'll need to implement a process to segment them into smaller chunks before sending them for processing.
An integrated platform like eesel AI offers predictable pricing and eliminates the extensive development work required to handle real-time audio streams, data integration, and scalability. It allows businesses to deploy a voice agent in minutes rather than months, with transparent costs.
Share this post

Article by
Kenneth Pangan
Writer and marketer for over ten years, Kenneth Pangan splits his time between history, politics, and art with plenty of interruptions from his dogs demanding attention.







