
If your company runs on Salesforce, it's the center of your universe for customer data. So, integrating an AI chatbot probably feels like the next logical move. You're trying to make your support team more efficient, keep customers from getting frustrated, and maybe, just maybe, reclaim some of your evenings.
But actually getting a chatbot up and running can feel… complicated. A lot of teams get stuck before they even start. Should you use Salesforce's own Einstein Bots, or look at a third-party tool? It’s a decision that brings up a ton of questions about cost, complexity, and how long it’ll be before you see any real benefit.
This guide is here to clear things up. We'll walk you through a straightforward, step-by-step process for the implementation of AI chatbots in Salesforce. We'll look at the two main routes you can take, sticking with the native tools or bringing in a modern, integrated platform, so you can make a call that works for your team.
Prerequisites for implementing AI chatbots in Salesforce
Before you jump into building anything, it’s good to have your ducks in a row. What you'll need depends entirely on which path you choose.
Path 1: Using Salesforce Einstein Bots (the native approach)
If you're planning to use Salesforce's built-in tools, you’ll need to have a few things set up in your Salesforce org first. This path is powerful, for sure, but it expects you to be all-in on the Salesforce ecosystem.
-
Service Cloud License: First things first, you'll need this. It’s the foundation for Salesforce's whole customer service suite, which is where your bot will live.
-
Live Agent License: Your bot needs a way to chat with people, and in the Salesforce world, that’s Live Agent. This license turns on the real-time chat your bot will plug into.
-
Omni-Channel Setup: This sounds super technical, but it's basically the air traffic control for your support team. You’ll have to configure things like presence statuses (who's online), routing rules (which chats go where), and service channels to make sure conversations can move from your bot to a human without getting lost in the ether.
-
Salesforce Knowledge Base: An Einstein Bot is only as smart as the information you feed it. It mostly pulls answers from your Salesforce Knowledge articles. This means you’ll want to make sure your knowledge base is organized, up-to-date, and actually helpful.
Path 2: Using a modern third-party platform (like eesel AI)
Things are a lot simpler on this side of the fence. If you go with a more modern tool, the list of must-haves is much shorter because these platforms are built to connect to what you already have, without a ton of prep work.
-
A Salesforce Account: You'll obviously still need your Salesforce account. This is how the platform connects to your CRM to do useful things like create cases or pull up customer info.
-
An eesel AI Account: You can sign up and get going on a free trial all by yourself, often without ever having to talk to a salesperson.
-
Your Existing Knowledge Sources: This is the biggest difference. You don't have to migrate everything into Salesforce Knowledge. You can connect your existing help center, train the AI on past support tickets, and even pull information from other places your team works, like Confluence or Google Docs, with simple one-click integrations.

A step-by-step guide to implementing AI chatbots in Salesforce
Alright, ready to dive in? Here’s a no-fluff guide to take you from a rough idea to a live chatbot.
Step 1: Figure out your chatbot's purpose and scope
Before you get caught up in what your bot will say, you need a plan. Start by asking what you actually want this thing to do. What are the repetitive tasks that are bogging down your team? Are you drowning in "where's my order?" tickets, struggling to qualify leads, or spending way too much time on password resets?
Once you have a general idea, get specific. Pick three to five top use cases for the bot to handle at launch. Don't overcomplicate it. For example:
-
Answer "Where is my order?"
-
Help with password reset requests.
-
Create a support case in Salesforce.
With your use cases sorted, think about what success looks like. Are you trying to lower your case volume, bump up your customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores, or get more qualified leads? Setting clear goals from the start makes it way easier to know if your chatbot is actually pulling its weight later on.
Step 2: Choose your implementation path
This is the fork in the road. Your choice here will pretty much define the rest of the project. You're deciding between building inside the Salesforce "walled garden" or using an external tool that plugs into it.
The Salesforce Einstein Bots path is a solid choice if your team lives and breathes Salesforce and you need really deep, custom integrations with your Salesforce objects and flows. Just be ready for a longer setup. It often requires someone with specialized Salesforce skills (or a consultant on speed dial) and can be a headache if your company knowledge is scattered across different apps.
On the other hand, a modern third-party platform like eesel AI is built for speed and flexibility. The setup is self-serve and can be done in an afternoon, not over several months. This approach lets you connect all your knowledge sources, not just what's in Salesforce, and gives you more intuitive control over the bot's behavior without writing any code. For most teams, it's the faster and more direct route to getting a helpful bot in front of customers.
Step 3: Connect your knowledge sources
A chatbot without knowledge is just an empty chat window. How you get that knowledge into its brain depends on the path you're on.
If you’re building with Einstein Bots, your main job is to get your Salesforce Knowledge articles in tip-top shape. The bot's ability to answer questions is directly linked to how good that internal database is. You'll need to spend time tagging, categorizing, and updating articles to feed the bot.

With a platform like eesel AI, you can cast a much wider net. Instead of just relying on formal help articles, you can train your AI by connecting your past Salesforce support tickets. This is a huge leg up because the AI learns your brand's voice and finds solutions from real-world conversations. From there, you can easily plug in other sources with one-click integrations, like your public help center, internal wikis, or random Google Docs. This gives the AI a complete picture of your business, not just the polished, official version.

Step 4: Build your chatbot's logic and actions
Now for the fun part: designing the conversation.
Inside Salesforce, you’ll use the Einstein Bot Builder to map out "Dialogs," which are basically conversational flowcharts. To make the bot do things, like create a case or look up an order, you’ll have to connect these dialogs to Salesforce Flows. This is great if you’re a Salesforce automation guru, but it can feel like learning a new language if you’re not.

In contrast, eesel AI keeps things simple with a natural language prompt editor and a feature called 'AI Actions'. You can define the bot's personality and tell it when to pass a chat to a human, all in plain English. For more complex tasks, like checking an order status in Shopify or updating a ticket, you can set up custom API calls through an easy-to-use, no-code interface. It gives you full control over what the bot does without needing a developer.
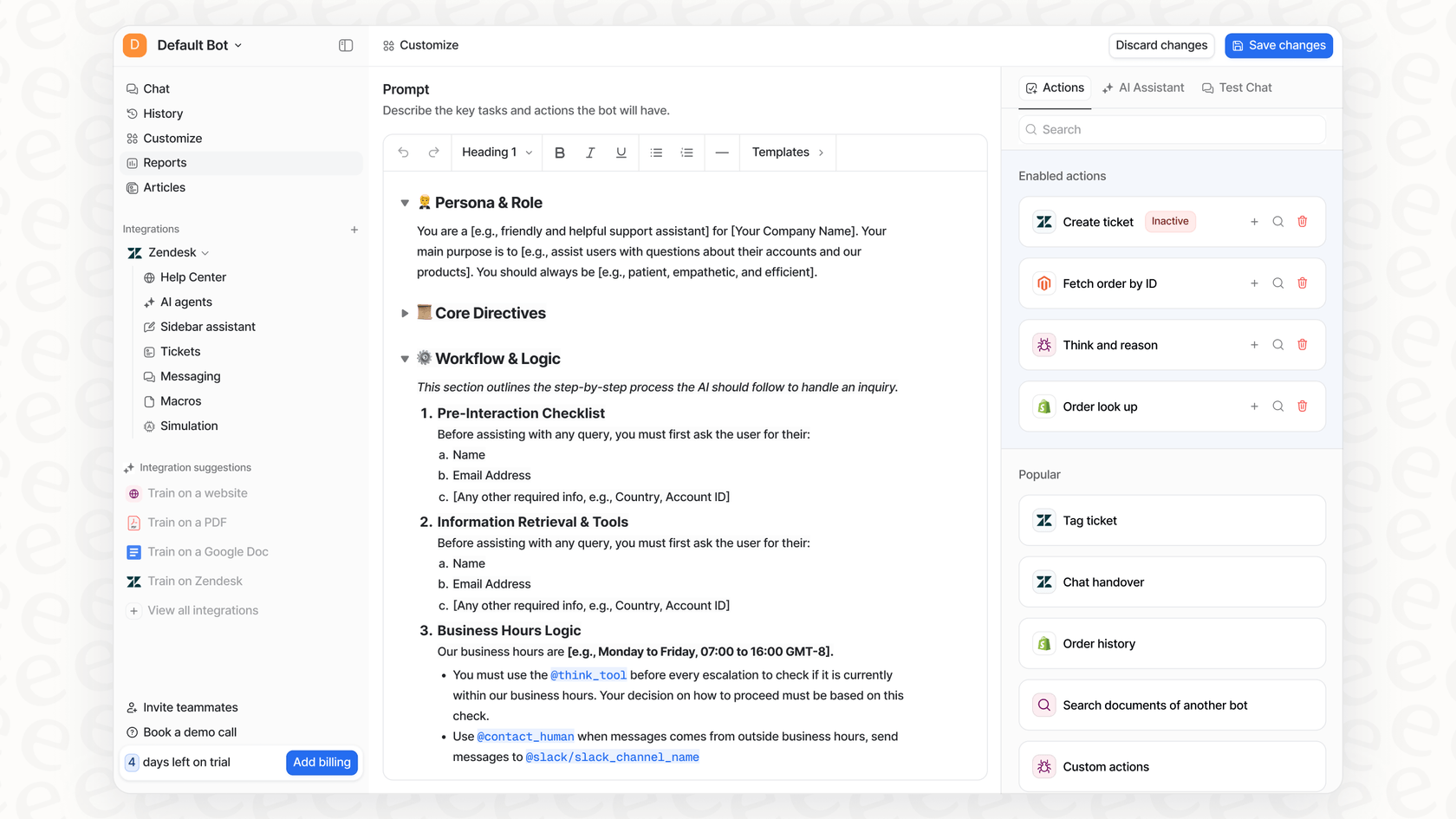
Step 5: Test and simulate your chatbot before going live
You wouldn’t launch a new website without testing it, right? Same goes for your chatbot.
With a native Salesforce bot, testing is a pretty manual job. You’ll open a preview window and type in questions, pretending to be a customer, trying to see if you can break it or find weird dead ends in the conversation.

This is where eesel AI completely flips the script with its Simulation Mode. Before a single customer talks to your bot, you can run it against thousands of your actual past Salesforce tickets. The simulation spits out a report showing you its predicted resolution rate, the exact answers it would have given to real questions, and where you might have gaps in your knowledge. This lets you launch feeling confident, with a data-backed forecast of how it's going to perform.
Step 6: Deploy and monitor your chatbot
Once you're happy with how it's performing in tests, it's time to go live. For an Einstein Bot, this means hooking it up to your chat deployment and flipping the switch.
With a tool like eesel AI, you can roll it out more gradually. For instance, you could activate the AI to handle only tickets from a specific email address or those with a certain tag. This lets you ease into automation without a big, scary launch day.
After launch, keep an eye on how it’s doing. Check your goals and read through conversation transcripts to see where the bot is doing great and where it’s fumbling. The analytics dashboard in eesel AI doesn't just show you performance numbers; it also spots trends and suggests new knowledge base articles based on conversations it has successfully resolved. This creates a nice little loop for continuous improvement.
This video provides a comprehensive tutorial on the implementation of an Einstein Chatbot in Salesforce, taking your customer service to the next level.
Common mistakes to avoid during implementation
Getting a chatbot live can be pretty smooth, but a few common slip-ups can derail your project. Here's what to watch out for:
-
Trying to do everything at once: It’s tempting to build a bot that can solve every problem from day one, but that's a surefire way to get overwhelmed. Start with a narrow, clear scope (your top 3-5 use cases) and expand from there. Nail the basics first.
-
Forgetting the escape hatch: Nothing makes a customer angrier than being stuck in a loop with a bot that can't help. Make sure there's always an obvious, easy way to talk to a human. Your bot should be a helpful assistant, not a gatekeeper.
-
Using a limited knowledge base: If you only train your bot on formal, jargon-heavy help articles, it's going to sound stiff and unhelpful. Training it on real, historical conversations (a core feature of eesel AI) helps it pick up your brand's voice and learn how your best agents actually solve problems.
-
Skipping the dress rehearsal: Going live without proper testing is a gamble. Using a simulation environment, like the one we covered in Step 5, is the single best way to lower that risk and make sure your launch goes off without a hitch.
Your path to smarter Salesforce support
The implementation of AI chatbots in Salesforce is one of the best ways to scale your support, but your approach is everything. While native tools like Einstein Bots offer deep integration, they often come with a lot of complexity and a much slower path to getting any real value.
Modern, self-serve platforms give you a faster, more flexible, and often more powerful option. By bringing all of your company's knowledge together and providing smart features like risk-free simulation, these tools let you launch an intelligent chatbot that actually helps your customers and your team.
Get your Salesforce AI chatbot running in minutes, not months
Ready to skip the long setup and complicated implementation? With eesel AI, you can connect Salesforce, train an AI on your real customer conversations, and launch a powerful support agent in a single afternoon. Simulate its performance on your past tickets and go live with the confidence that you're automating support the right way.
Frequently asked questions
Many teams struggle with the initial complexity of choosing between native Salesforce tools or third-party platforms, as well as integrating disparate knowledge sources. Getting a chatbot up and running effectively often feels complicated due to these factors.
Salesforce Einstein Bots offer deep, native integration but typically require more specialized Salesforce skills and a longer setup time. Modern third-party platforms, like eesel AI, are designed for faster, self-serve setup and can connect to a wider array of knowledge sources beyond just Salesforce Knowledge.
If using Einstein Bots, you'll need Service Cloud, Live Agent licenses, Omni-Channel setup, and a well-organized Salesforce Knowledge Base. For a modern third-party platform, you primarily need your Salesforce account and an account with the platform itself, as it connects to your existing knowledge sources directly.
Testing is crucial to ensure your chatbot works as expected and avoids customer frustration. While native bots often require manual testing, modern platforms like eesel AI offer a "Simulation Mode" to test against thousands of past support tickets, providing data-backed performance forecasts before going live.
To achieve a natural and helpful tone, train your AI chatbot on diverse, real-world knowledge sources, including past support conversations, not just formal articles. This helps the bot learn your brand's voice and typical solutions, avoiding a stiff or unhelpful demeanor.
Avoid trying to automate everything at once; start with 3-5 key use cases. Always provide an obvious "escape hatch" for customers to connect with a human. Also, don't limit your bot to a narrow knowledge base, and thoroughly test it using simulation before deployment to reduce risks.
Share this post

Article by
Kenneth Pangan
Writer and marketer for over ten years, Kenneth Pangan splits his time between history, politics, and art with plenty of interruptions from his dogs demanding attention.







