If you're a Jira admin or project manager, your day is probably a juggling act. Between breaking down massive projects, writing the perfect query, and triaging an endless stream of support tickets, the "work about work" can easily swallow up the time you'd rather spend on actual strategy.
Atlassian has integrated powerful AI features directly into Jira, providing a robust foundation for modern teams. This guide will walk you through, step-by-step, how to use AI in Jira to maximize these capabilities. We’ll start with the native tools that excel at project management and then look at how you can set up a smart, integrated AI agent to complement your frontline support and help you get even more time back in your day.
How to use AI in Jira: What you'll need to get started
Before we jump in, just make sure you have these things ready:
-
An active Atlassian Jira Cloud account.
-
Admin or project admin permissions so you can set up automations and integrations.
-
A rough idea of which repetitive tasks or support questions you'd like to automate.
A step-by-step guide to using AI in Jira
Here’s a practical, four-step approach to bringing AI into your Jira setup, starting with the capable built-in features and moving up to more advanced automation options.
Step 1: Automate project management with native Jira AI
Atlassian has been integrating its own AI, called Rovo (or Atlassian Intelligence), to help with the more detailed parts of project management. These tools are a fantastic place to start if you're looking to boost productivity.
Generate JQL queries with plain English
Jira Query Language (JQL) is a powerful tool with a lot of depth. Instead of having to memorize the exact syntax for every search, you can now just type what you want in plain English, like "unresolved issues assigned to me due this week." The AI translates that into a perfect JQL query. It saves a ton of time and makes advanced search available to everyone on the team, regardless of their JQL experience level.
Break down epics into smaller tasks
Managing a large epic is much easier with AI. With Jira's AI features, you can ask it to scan an epic's description and suggest a logical breakdown of child issues. You can look over the suggestions, make a few tweaks, and then create them all with one click. It's a massive time-saver during project planning sessions.
Summarize long comment threads
Catching up on a ticket with many comments is a common challenge. Instead of reading through everything to find a specific update, you can use the AI summary feature. It reads the conversation and pulls out key decisions and action items, so you can get up to speed in seconds.
Create automation rules with a simple prompt
Jira’s built-in automation builder is highly capable, and AI makes it even easier to use. You can give it a prompt like, "When a high-priority bug is reported, assign it to the development team lead," and the AI will build the automation rule for you.
These native features are excellent for managing tasks within the Atlassian ecosystem. While they are highly optimized for internal workflows, you can further extend this power by connecting Jira to knowledge sources that exist outside of your Atlassian products.
Step 2: Beef up your knowledge base for self-service
One of the most effective ways to use AI is to help users find the right documentation quickly. Jira and Confluence provide a strong starting point for this self-service experience.
Use AI to draft and refine help articles
When you solve a support ticket, that solution is valuable information for the future. Agents can use AI right inside a Jira ticket or a Confluence page to brainstorm a new help article. Features like "improve writing" or "change tone" help you quickly turn a specific solution into a professional, consistent article for your knowledge base.
Connect your knowledge base to Jira Service Management
Once you have a solid set of articles in Confluence, you can link that space to your Jira Service Management project. This allows Jira's virtual agent to suggest relevant articles to users as they type in the help portal, often answering their question before they even submit a ticket.
To build on this foundation, some teams also choose to bring in knowledge from other platforms - like Google Docs, Notion, or Slack - to complement their Confluence setup and create a more comprehensive support experience.
Step 3: Set up a true AI agent for frontline support
Once you've maximized the value of native features, you might consider adding a specialized AI agent that can connect all your knowledge sources and perform complex actions across different platforms.
Expanding the capabilities of native virtual agents
Native virtual agents are excellent for managing a single, well-organized knowledge base within Jira. For more complex needs, teams often look for complementary tools that can bridge the gap between platforms. These specialized agents can access information outside of Confluence, learn from the context of historical tickets across various systems, or perform specialized actions like tagging tickets and looking up external customer data.
How to connect a powerful AI agent to Jira Service Management
To build the most flexible support system, you can use an AI that complements your Atlassian tools. Tools like eesel AI are built to plug directly into the Jira ecosystem, making your existing setup even more powerful.
Getting it up and running is straightforward:
-
Sign up and connect Jira: You can get started in a few minutes with a simple one-click integration that works alongside your existing Jira Cloud account.
-
Unify your knowledge sources: You can connect Confluence, Google Docs, Notion, SharePoint, and your historical support tickets. This gives your AI a complete picture of your business to better serve your customers.
-
Customize your AI's persona and actions: With an easy-to-use editor, you can define your AI's tone and give it the power to take specific actions. You can configure your AI Agent to triage tickets by adding tags or making API calls to fetch details from other business systems.

Step 4: Test and roll out your AI with confidence
When introducing AI to your support workflow, a controlled rollout ensures a smooth experience for both your team and your customers.
Use simulation to see how it will perform
To understand exactly how an AI will behave, you can use a simulation mode. Tools like eesel AI allow you to run your configured agent against thousands of past tickets in a safe environment.
This shows you exactly how the AI would have responded to real questions, giving you a clear forecast of its performance and helping you identify any areas where your knowledge base could be strengthened. You can refine its behavior with confidence before it ever interacts with a customer.

Roll out gradually and keep an eye on things
You can start by automating specific, high-volume ticket types - such as password resets or billing inquiries - while keeping your human team focused on more complex cases. As you see the positive results, you can gradually expand the AI's responsibilities.
Tips for getting the most out of AI in Jira
-
Start with the biggest time-wasters. Identify the top 3-5 most repetitive tasks your team handles. Automating these first will provide the most immediate value to your workflow.
-
Focus on support and project efficiency. Jira's AI is incredibly strong at handling conversational support and streamlining project management. Use these features to handle the day-to-day work so you can focus on high-level strategy.
-
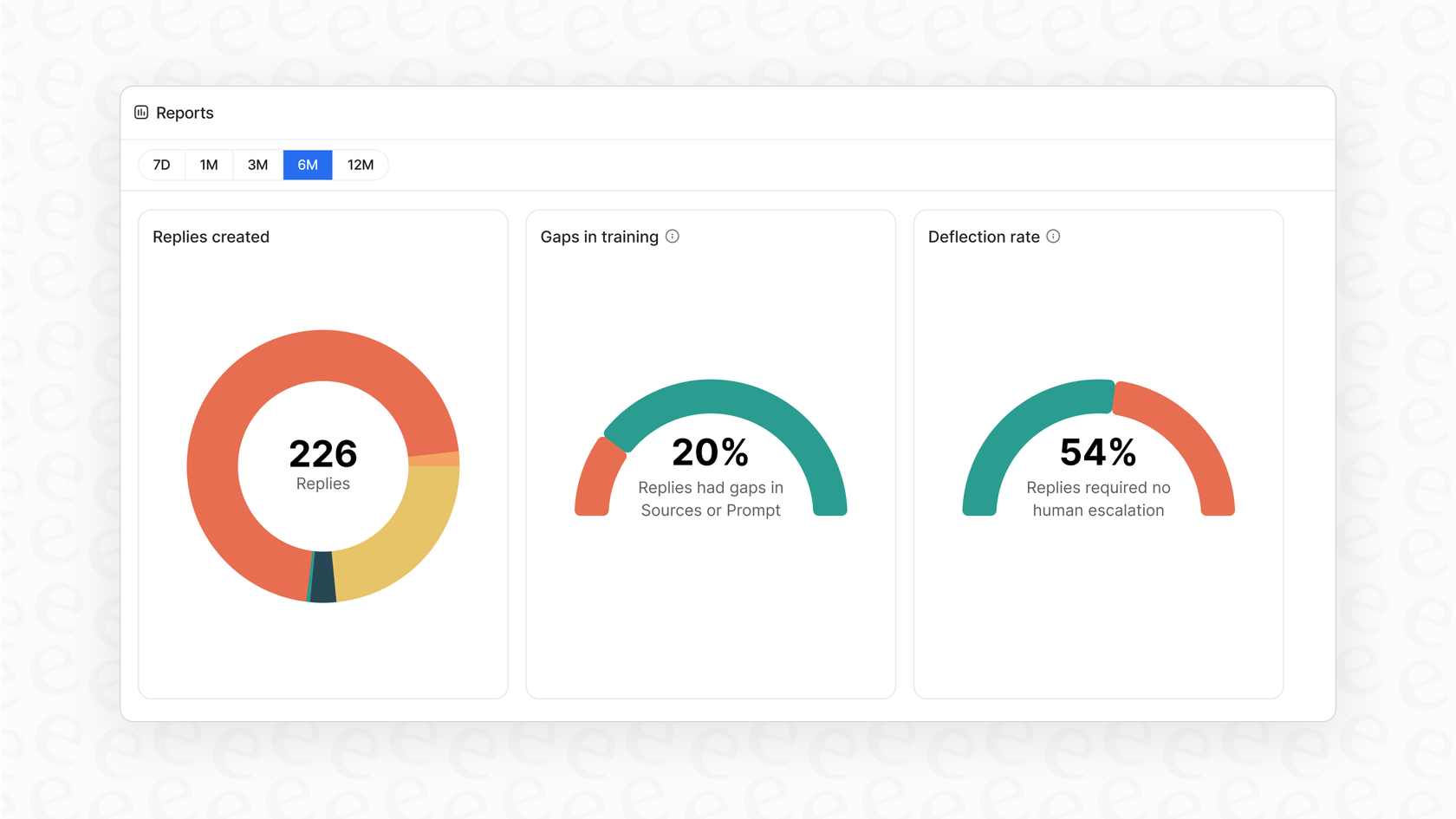
Keep improving your knowledge base. Your AI thrives on accurate information. Use insights from your tools, like the knowledge gap reports in eesel AI, to see what users are asking and keep your documentation up to date.
Moving beyond basic automation
As you can see, using AI in Jira is a journey. You can start today with powerful native features to streamline your project management. To further enhance your team's efficiency and provide instant support, you can integrate specialized agents that learn from all your knowledge sources and work seamlessly with your helpdesk.
Ready to see how a fully integrated AI agent could work with your Jira Service Management? Get started with eesel AI for free.
Frequently asked questions
Learning how to use AI in Jira can significantly reduce time spent on repetitive tasks like generating JQL queries, breaking down epics, and summarizing comment threads. For support teams, it enables faster ticket resolution and improved self-service, freeing up human agents for more complex issues.
Atlassian's native AI features primarily enhance internal project management tasks within Jira and Confluence, like drafting content or building automation rules. A dedicated AI agent can connect to external knowledge sources (like Google Docs or Slack) and perform actions like triaging tickets or making API calls, extending AI capabilities beyond the Atlassian ecosystem.
A robust knowledge base is crucial because AI agents rely on accurate and comprehensive information to provide relevant answers. By using AI to draft and refine help articles and connecting your knowledge base to Jira Service Management, you empower the AI to deflect common inquiries and provide immediate self-service solutions.
Integrating an external AI agent typically involves connecting it directly to your Jira Cloud account, then unifying all your scattered knowledge sources (Confluence, Google Docs, past tickets, etc.). You can then customize the AI's persona and define specific actions it can take, often without complex coding or lengthy development cycles.
Before full deployment, utilize simulation modes offered by tools like eesel AI to test your agent against thousands of past tickets in a risk-free environment. This allows you to forecast its performance, identify knowledge gaps, and refine its behavior. Gradually roll out the AI, perhaps starting with high-volume, low-complexity ticket types, while continuously monitoring its effectiveness.
Native Atlassian Intelligence is highly optimized for knowledge residing within Confluence or Jira. To extend these capabilities to external platforms like Google Docs or Notion, or to learn from the context of historical tickets across various systems, teams often use complementary AI agents that bridge the gap across different ecosystems.
Share this post

Article by
Kenneth Pangan
Writer and marketer for over ten years, Kenneth Pangan splits his time between history, politics, and art with plenty of interruptions from his dogs demanding attention.






