
You’ve probably seen the buzz around OpenAI's "gpt-realtime" and its smaller sibling. If you've scrolled through tech Twitter or caught the announcement, you might be wondering what all the fuss is about. There's a lot of chatter, and frankly, a lot of confusion about what these new models are, what they can do, and how they’re any different from what we already had.
This guide is here to cut through that noise. We’re going to break down exactly what GPT realtime mini is, what it’s actually good for, and how you could use it for something practical, like customer support, without needing a degree in computer science. We'll also take an honest look at its features, costs, and limitations so you get the full picture.
What is GPT realtime mini?
First, let's get the name straight. If you dig into OpenAI's documentation, you'll see the official model is called "gpt-4o-mini-realtime-preview". That’s a bit of a mouthful, so for the rest of this guide, we'll just call it GPT realtime mini. It's the smaller, quicker, and more budget-friendly version of the main "gpt-realtime" model.
So, what makes it a big deal? GPT realtime mini is a native speech-to-speech model. This is a pretty major shift from how voice AI used to work. In the past, creating a voice agent was like a clunky, three-step relay race. First, a speech-to-text model would transcribe what you said. Then, a language model like GPT-4 would figure out what to say back. Finally, a text-to-speech model would read that response aloud. Each handoff added a little bit of lag, creating those awkward pauses that make AI conversations feel so unnatural.
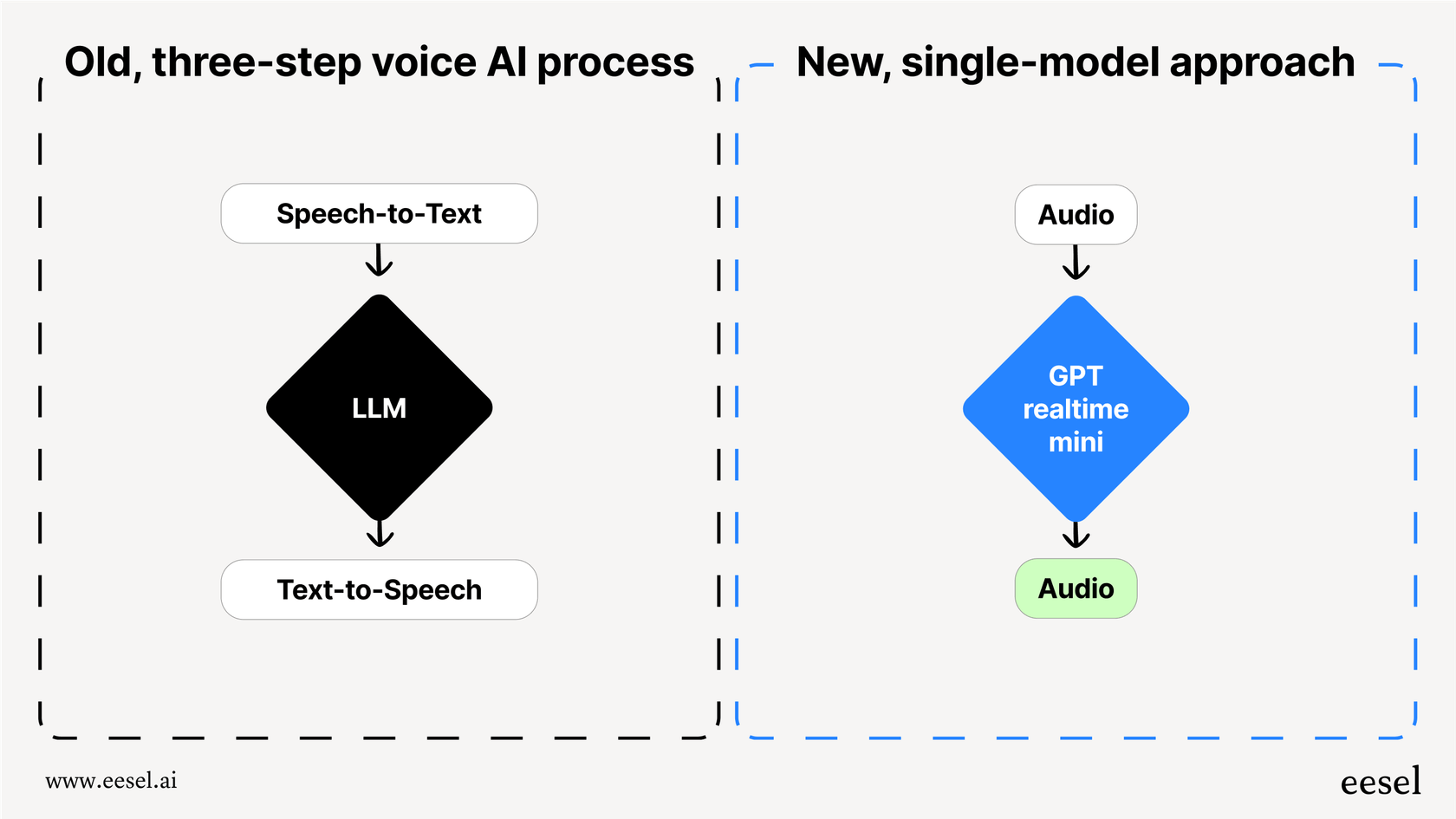
GPT realtime mini handles everything in one seamless process. It listens to audio and generates audio in response, cutting out the middlemen. This single-model approach drastically reduces latency, making conversations feel much more fluid and human. It can even pick up on your tone and adjust its own, something the old, pieced-together systems could never quite get right.
Key capabilities: What can it actually do?
Beyond just being fast, GPT realtime mini has a few core abilities that make it a powerful tool for building voice agents. Let's look at what they mean in the real world.
True speech-to-speech interaction for natural conversations
Because it processes audio directly, GPT realtime mini gets rid of those weird delays that make other voice AI systems feel clunky. We’ve all been on a call where a few seconds of dead air makes the conversation feel stilted and frustrating. By responding almost instantly, this model makes it possible to have a back-and-forth that feels like you're talking to a person, not a script.
OpenAI also introduced new, more expressive voices like "Marin" and "Cedar" with this model. They're a huge improvement over the robotic tones we're used to, making the whole experience feel more engaging.
Multimodal inputs for richer context
GPT realtime mini isn’t limited to just your voice. It’s built to process audio and text at the same time. For example, imagine a customer calling your support line while simultaneously typing their order number into a chat window on your website. The AI can take in both pieces of information at once to understand the full context and solve the problem faster.
The bigger, more expensive "gpt-realtime" model can even handle images. This opens up some pretty wild possibilities, like a customer sending a photo of a broken product and the AI being able to "see" it and walk them through the repair step-by-step.
Function calling for real-world tasks
This is where things get really useful. "Function calling" is a feature that lets the AI do more than just talk; it can actually do things. It allows the model to connect with other software and services to pull information or perform actions.
Here are a few examples of what that could look like:
-
A customer asks, "Where's my package?" The AI can use a function call to check the order status in your Shopify store and provide a real-time update.
-
A client wants to book a meeting. The AI can check your calendar through an API and schedule the appointment for them.
-
An employee needs to report an IT issue. The AI can create a ticket directly in your Jira Service Management system.
But here’s the thing: the API only gives you the toolkit. Your engineering team still has to build, host, and maintain every single one of these connections. It's a huge project that eats up a ton of developer time. This is where using a dedicated platform makes a lot of sense. Instead of building from the ground up, a solution like eesel AI comes with ready-made actions for tools like Zendesk and Gorgias. You can connect your helpdesk in a few clicks and build custom actions using a simple interface, no developer team required.

Practical use cases and implementation paths
So, the potential is clear. But how do you turn this cool tech into a working voice agent that actually helps your customers or your team?
Real-world examples
Here are a few ways businesses are already using this kind of technology:
-
24/7 Phone Support: An AI agent can answer your phones around the clock, handling common Tier 1 questions like "What are your hours?" or "How do I reset my password?" If a question is too complicated, it can intelligently transfer the call to the right human agent, along with a summary of the conversation so far.
-
Proactive Outbound Calls: Instead of your team spending hours on the phone, an AI can handle proactive outreach. It can call to confirm appointments, let a customer know their delivery is nearby using live data from a tracking system, or follow up on a recent support ticket.
-
Internal IT Service Desk: You can free up your IT team from endless repetitive queries. An internal voice assistant can manage password resets, troubleshoot common software problems, and log IT tickets automatically, letting your team focus on bigger issues.
The two paths to building a voice agent
When it comes to actually building this, you have two main options: you can go the do-it-yourself route with the OpenAI API, or you can use a dedicated platform.
The DIY path offers total flexibility, but it's a long and expensive journey. You'll need to hire developers to set up the connection using WebRTC or WebSockets, manage authentication, build and host all the function-calling tools, link up your different data sources, and create your own analytics dashboard to track performance. It's a massive undertaking that can easily take months to get running.
The platform path is designed to let you skip all that. A platform like eesel AI is built to be self-serve. You can sign up, connect your helpdesk and knowledge bases with a few clicks, tweak your AI's personality and actions from a simple dashboard, and have a voice agent live in minutes. The goal is to let you go live in minutes, not months, without having to write a single line of code.
Understanding the real cost
One of the biggest sources of confusion online is the cost. The pricing model is a bit complicated, and the API fees are only part of the story.
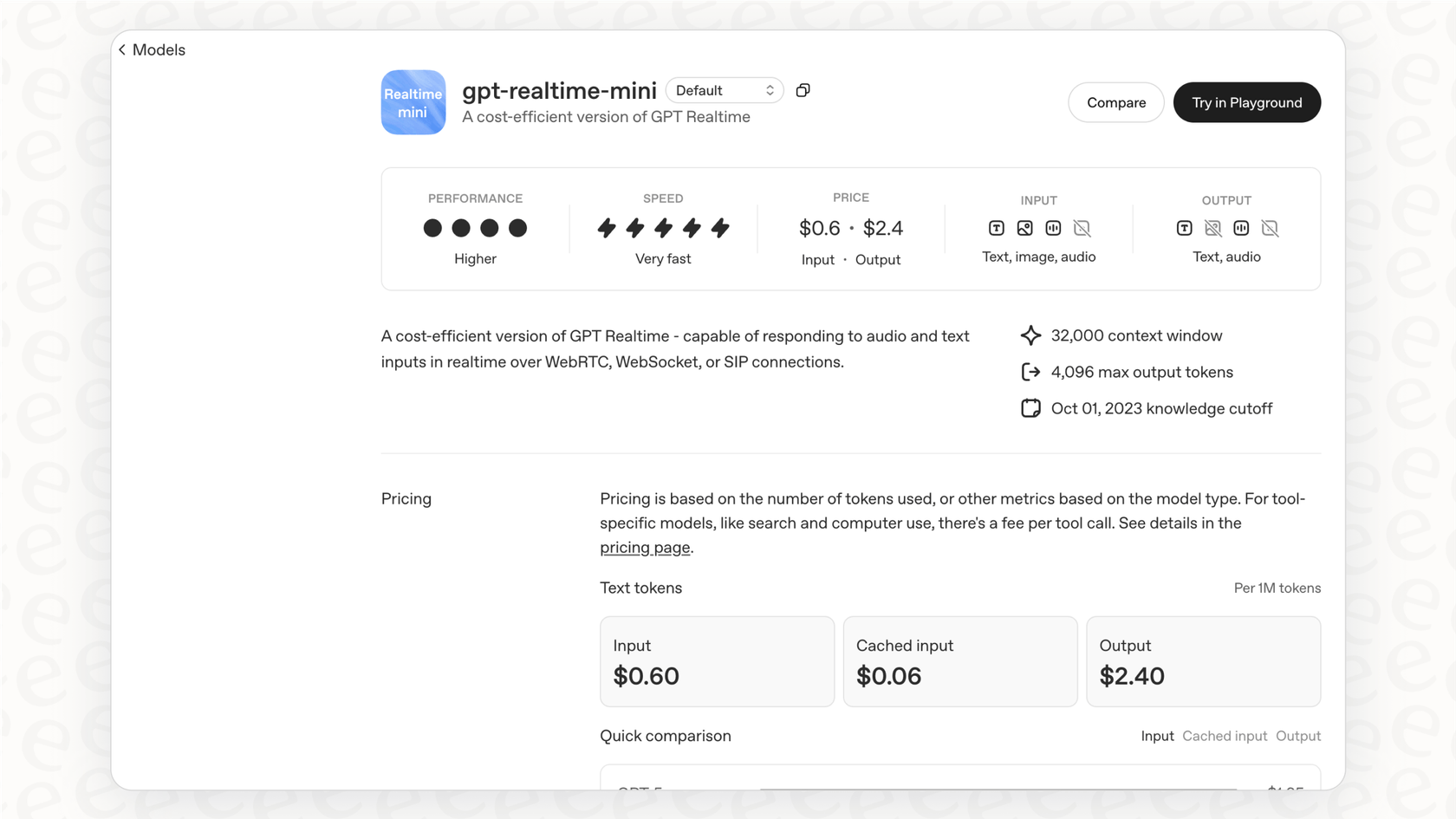
The API pricing explained
OpenAI prices its models based on "tokens," which is just a way of measuring data. For speech-to-speech models, you're billed for both the audio you send (input) and the audio the model sends back (output). As you can see from the table below, audio tokens are quite a bit more expensive than text tokens.
Here's the official breakdown for "gpt-4o-mini-realtime-preview", priced per 1 million tokens:
| Modality | Input Cost | Cached Input Cost | Output Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Text | $0.60 | $0.30 | $2.40 |
| Audio | $10.00 | $0.30 | $20.00 |
Source: OpenAI Pricing
The unpredictable nature of token usage can make it incredibly difficult to forecast your costs. A slightly longer conversation or a bit of background noise could cause your bill to jump unexpectedly.
The hidden costs of development and maintenance
The API fees are just the beginning. The real expense of a DIY voice agent comes from the team you need to build and keep it running. You have to account for developer salaries, server costs, and the time spent monitoring, debugging, and improving the system. These hidden expenses can easily add up to more than the API fees themselves.
This is another reason why a managed solution can be a better choice. Platforms like eesel AI offer transparent and predictable pricing based on a set number of interactions per month. You know exactly what your bill will be, with no confusing token math or surprise charges. This lets you budget properly and scale your support without worrying about costs spiraling out of control.
Limitations and how to overcome them
While GPT realtime mini is an amazing tool, it's not a silver bullet. The raw API has some big limitations you need to know about before you jump in.
First, there are the technical barriers. The official documentation is clear that using the Realtime API directly requires a solid grasp of technologies like WebSockets, WebRTC, and session management. It’s not a simple plug-and-play solution; it’s a tool for experienced developers.
Second, and maybe more importantly, is the challenge of deploying it safely. How can you be sure your voice agent is ready for real customers? What happens if it gives out wrong information or fails to escalate an urgent issue? The raw API doesn't give you a clear way to test your setup in a controlled environment.
This is where a platform-based approach is so important. For instance, eesel AI was designed to solve this problem with its powerful simulation mode. You can run your AI agent against thousands of your past support conversations in a safe, sandboxed environment. You get to see exactly how it would have responded to real customer questions, giving you an accurate prediction of its performance and automation rate. This lets you fine-tune its behavior, spot knowledge gaps, and test with confidence before it ever speaks to a single customer. You can then roll it out slowly, starting with simple queries and expanding its responsibilities as you build trust in its abilities.

The future of voice with GPT realtime mini is here, if you have the right tools
There's no question that GPT realtime mini is a groundbreaking piece of tech. It makes natural, conversational AI a reality and opens up all kinds of possibilities for automating customer interactions. But it's important to remember what it is: a powerful, low-level tool for developers, not an out-of-the-box solution for support teams.
Building a reliable, secure, and effective voice agent from scratch is a complicated and costly project. It requires a full platform to handle integrations, workflow automation, and, most critically, a safe way to test and deploy.
This video explores some of the real-world use cases for the GPT realtime mini model.
Ready to use the power of next-gen voice AI without the engineering headaches? Connect your helpdesk and see how eesel AI can transform your customer support. Start your free trial today.
Frequently asked questions
GPT realtime mini is a native speech-to-speech model that processes audio directly without an intermediate text conversion step. This dramatically reduces latency, making conversations feel much more fluid and natural compared to previous multi-step voice AI approaches.
GPT realtime mini eliminates the awkward delays typical of older voice AI systems by processing audio in one seamless flow. Additionally, it offers new, more expressive voices like "Marin" and "Cedar," which significantly enhance the conversational experience to feel more engaging and human.
Function calling allows GPT realtime mini to connect with external software and services to perform real-world actions. For example, it can check order statuses in your e-commerce store, book appointments on a calendar, or automatically create support tickets in systems like Jira.
Businesses are deploying GPT realtime mini for 24/7 phone support, handling routine inquiries and intelligently routing complex calls to human agents. It's also used for proactive outbound communications, such as confirming appointments, and to automate internal IT service desks for tasks like password resets and ticket logging.
OpenAI prices GPT realtime mini based on "tokens" for both input and output audio, which can be difficult to predict. Beyond these API fees, significant hidden costs include developer salaries, server hosting, and ongoing maintenance, making DIY implementations costly and unpredictable.
Direct implementation requires expertise in technologies like WebSockets and WebRTC, and safely deploying an untested agent to customers is a major risk. Platforms like eesel AI address this with powerful simulation modes, allowing you to test against past conversations and fine-tune performance before live deployment.
Share this post

Article by
Kenneth Pangan
Writer and marketer for over ten years, Kenneth Pangan splits his time between history, politics, and art with plenty of interruptions from his dogs demanding attention.







