If you hang around software development circles, you've probably heard the term "agentic coding" pop up. It’s a bit of a buzzword, but the idea behind it is pretty straightforward: AI is moving from being a simple code suggestion tool to a full-blown collaborator that can handle tasks on its own. Anthropic's Claude Code is a major player in this space, and its integration with GitHub Actions is fundamentally changing how teams write, review, and fix code. It’s like having an incredibly fast junior developer join your team.
This guide will break down what the Claude Code GitHub integration is, how it actually works, and what it’s genuinely good at. We’ll cover the main uses, some best practices, and (just as important) its limitations. By the end, you'll have a clear picture of where it fits in your workflow and where you might need a different kind of tool.
What is the Claude Code GitHub integration?
To really get what this integration does, it helps to understand the two pieces of tech involved. They’re both powerful on their own, but they create something entirely new when they work together.
What is Claude Code?
Think of Claude Code as an AI coding assistant from Anthropic that’s built to understand, write, and rework code. It's much more than a simple autocomplete tool because it can grasp the context of an entire project. Developers usually interact with it through a command-line interface (CLI), which just means they type commands into their terminal. This makes it feel like a natural part of their day-to-day workflow.
What are GitHub Actions?
GitHub Actions is the automation engine built right into GitHub. You can think of it as a way to create simple rules for your code repository. For instance, you can set up a rule that says, "Whenever a developer pushes new code, automatically run all our tests to make sure nothing broke." It’s a handy way to automate the repetitive but essential tasks that keep a software project running smoothly.
When you combine them, the Claude Code GitHub integration lets you plug Claude Code directly into those automated workflows. The result is an AI that can be triggered by events in your GitHub repository, like a new comment or a pull request, to perform complex coding tasks all by itself. No developer has to run a single command on their own machine.
How the integration works
So, how does a simple comment in a GitHub issue magically get turned into a finished feature? It’s not magic, but it is a clever workflow that pieces together a few key components. Here’s a quick look at how it all connects.
Integration trigger: @claude mention
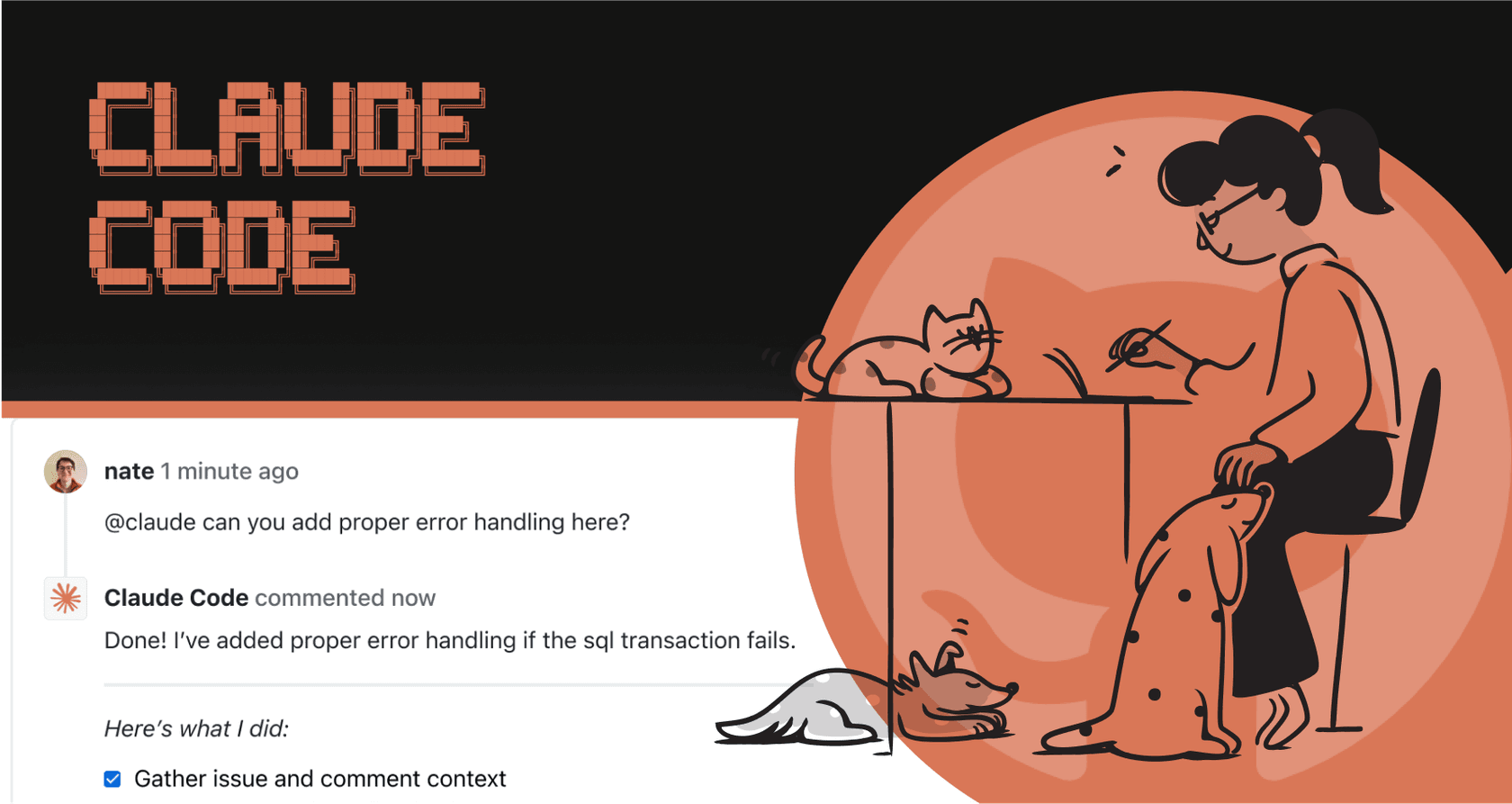
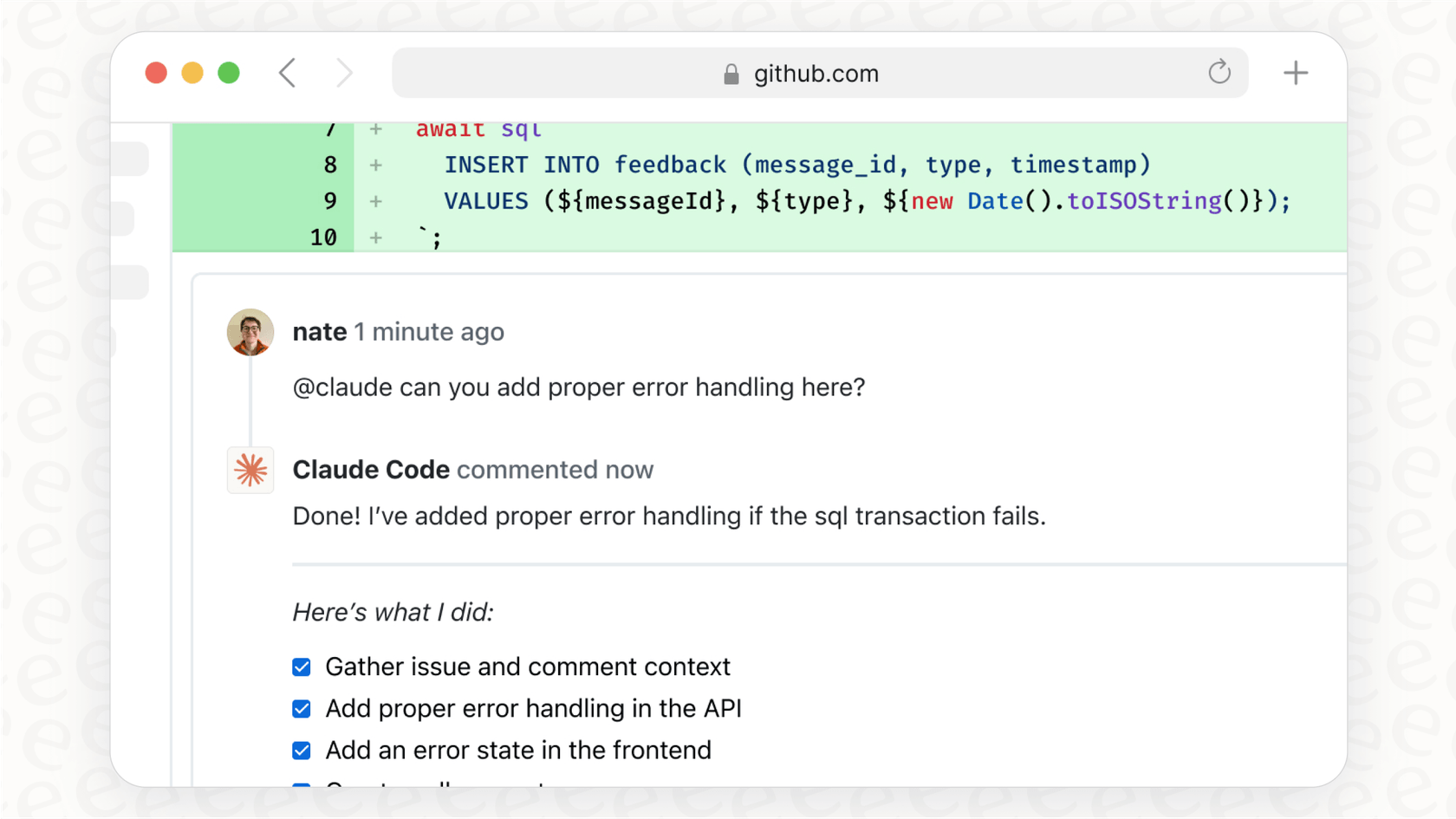
The whole process usually kicks off when someone mentions @claude in a pull request or an issue comment. It’s a lot like tagging a coworker to get their eyes on something. When a developer types @claude review this PR or @claude fix this bug, GitHub Actions wakes up, recognizing that the AI has been called in to help.
Integration playbook: The claude.yml file
Behind the scenes, a file in your repository called claude.yml acts as the instruction manual. This file, written in a format called YAML, tells GitHub Actions exactly what to do when it sees the @claude trigger. It contains the specific prompts and commands for the AI, like telling it to focus on code quality during a review or to follow the steps in an issue when building a new feature.
Integration brain: CLAUDE.md and repository context
Claude doesn’t just guess what to do. It gets its context from two main places: the entire codebase and a special file named CLAUDE.md. This file is where your team can jot down project-specific rules, coding style guides, and common commands. By reading this file, Claude makes sure its contributions, whether it's writing new code or suggesting changes, line up with the project's existing standards, just like any other developer on the team would.
The whole thing can be mapped out like this:
Key use cases for the GitHub integration
This integration isn’t just a cool tech demo; it solves real problems for development teams by automating tasks that usually eat up a lot of time. Here are some of the most common ways teams are putting it to work.
Automated code reviews
Instead of waiting for a senior developer to find a free moment, anyone on the team can ask Claude for a review. By commenting @claude review this PR, you can get instant feedback on your code. Claude will check for potential bugs, style inconsistencies, and whether the code follows the best practices you've defined in your CLAUDE.md file. This doesn't just speed things up; it also helps maintain high code quality and frees up your senior engineers to tackle bigger architectural problems.
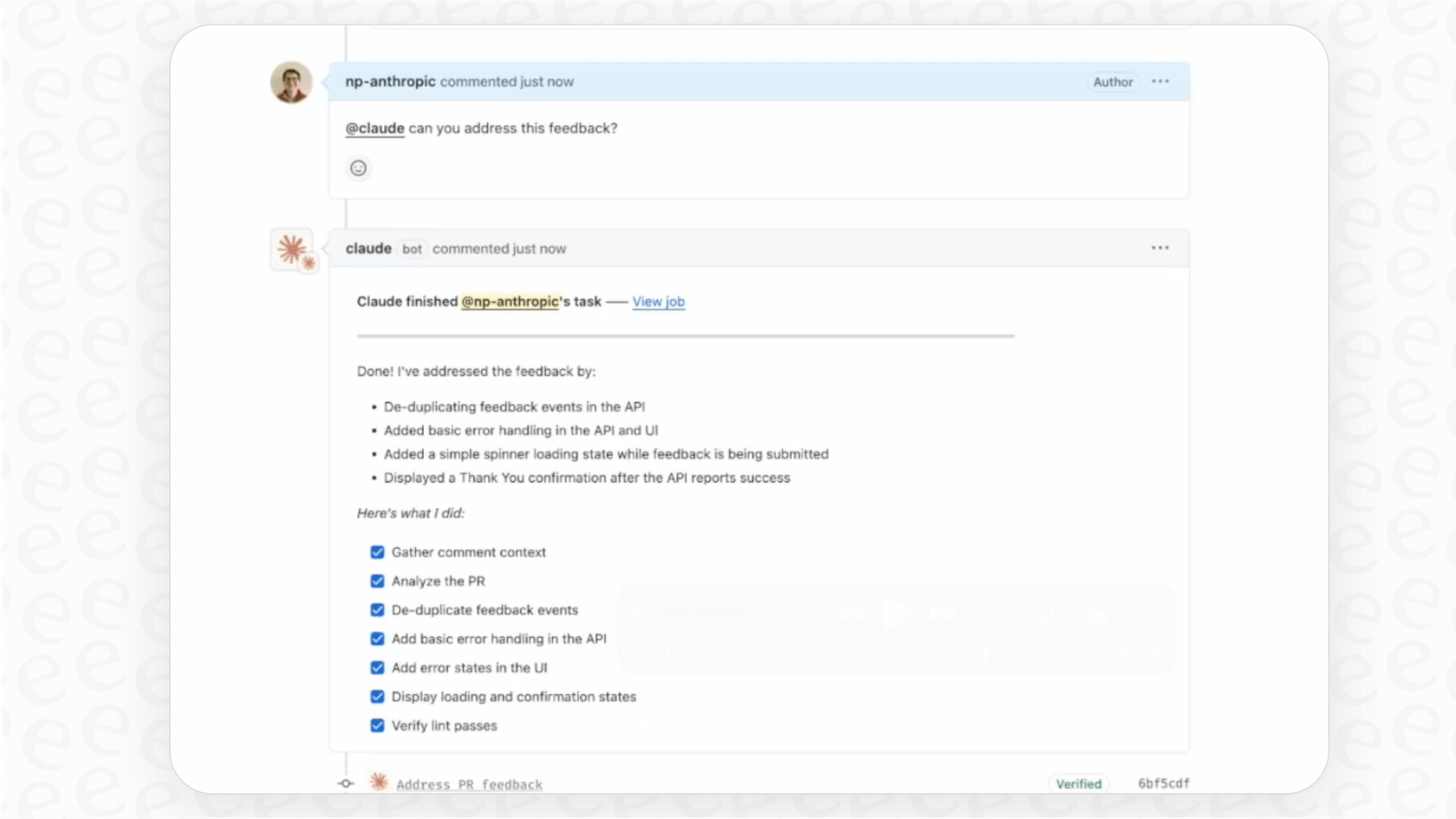
Building features automatically
This is where the "agentic" part really comes to life. A product manager or developer can create a new issue in GitHub laying out a feature request, like "Add user authentication to the login endpoint." Then, a developer can just comment @claude implement this on the issue. Claude will read the request, scan the codebase for context, write the necessary code, and then open a new pull request for a human to review. It effectively turns a feature ticket into working code with a single command.
Automated bug fixing
The process for fixing bugs is just as simple. When a user reports a bug and it gets logged as an issue in GitHub, a developer can assign it to Claude by commenting something like, @claude fix the TypeError in the user dashboard component. The AI will then dig into the codebase to find the source of the error, write the code to fix it, and submit the fix in a new pull request, often with a clear description of what it changed and why.
Answering codebase questions
Getting new developers up to speed on a large, complex codebase can take weeks. The Claude integration can act as a helpful guide. A new team member can pop into any issue and ask questions like, "@claude how does our billing system handle subscriptions?" or "@claude where are the main logging functions?" The AI will then search the codebase to find the answer and explain it. This seriously cuts down on onboarding time and means fewer interruptions for the rest of the team.
Setup, best practices, and limitations
While the Claude Code GitHub integration is powerful, it’s good to have realistic expectations. It’s a specialized tool built for a specific job, and understanding how to set it up, use it well, and know its limits is key.
A Claude Code GitHub Integration Setup
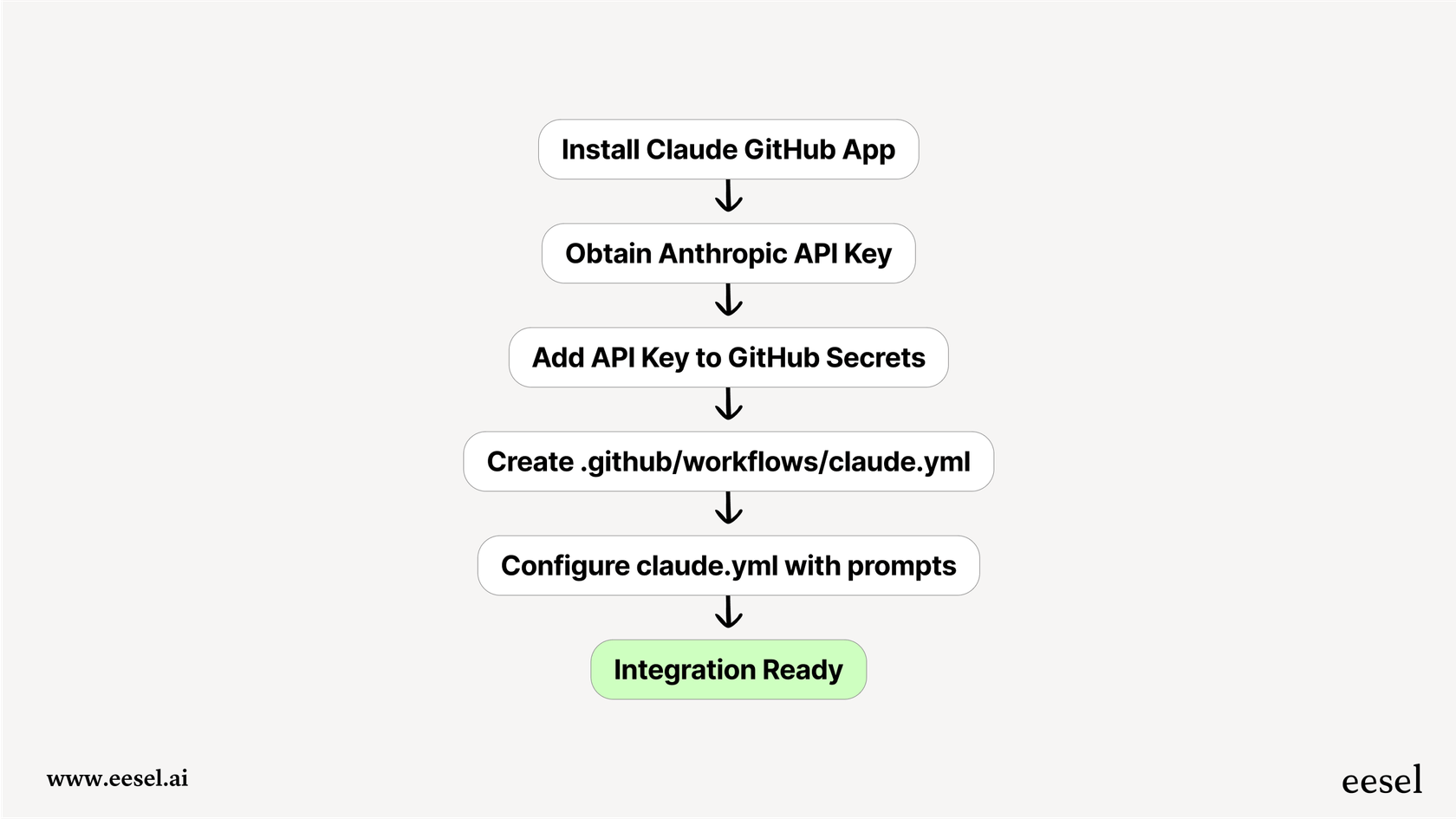
Getting started isn't a one-click process. It’s designed for developers and requires a bit of technical know-how. The main steps involve:
- Installing the Claude GitHub App on the specific repository where you want the AI to work.
- Getting an Anthropic API key and adding it to your repository's "secrets," which is GitHub's secure place for sensitive info.
- Creating a
.github/workflows/claude.ymlfile that defines the automation rules and prompts for Claude.
This process requires admin access to the GitHub repository and a decent understanding of how GitHub settings, secrets, and workflows operate.
Best practices for getting good results
To get the most out of Claude, it helps to follow a few simple guidelines:
- Be specific with your instructions. Vague prompts like "@claude fix it" will probably lead to vague or wrong results. A clear request like "@claude refactor the
calculate_totalsfunction to improve its performance and add comments" will give you much better code. - Use CLAUDE.md for project context. This is your main tool for teaching the AI about your team's unique standards. Keep it updated with your coding styles, common commands, and architectural rules to make sure Claude’s contributions are consistent with everyone else's.
- Iterate and give feedback. Don't expect a perfect, ready-to-merge solution on the first try, especially for complex tasks. Treat the AI like a junior developer. Review its work, provide feedback in follow-up comments, and guide it toward the right solution.
Integration limitations: It’s for code, not customers
This is where it’s really important to understand what the Claude Code GitHub integration is not. It’s a great example of using the right tool for the right job, and its strengths in software development are exactly what make it the wrong tool for other parts of the business.
This video demonstrates how the Claude Code GitHub integration can act as a virtual teammate, responding to feedback and fixing errors directly within a pull request.
- High technical barrier to entry: The entire setup and interaction model is built for software developers. It requires being comfortable with the command line, editing YAML configuration files, and managing API keys. It’s not a self-serve tool that a support manager or an IT lead could set up on their own.
- Limited knowledge sources: Claude’s world is the code inside your GitHub repository. While it's an expert on that, it can't connect to and learn from your other knowledge sources. It has no idea what’s in your Zendesk help center, your internal wiki in Confluence, or your team’s shared Google Docs. Its context is confined to code.
- Wrong tool for support automation: Because of its limited knowledge and developer-focused actions, it's just not built for automating customer support. It can't understand the nuance of a frustrated customer's ticket, sort incoming requests, or power a 24/7 customer chatbot. Its available "actions" are things like
git commitandcreate pull request, notescalate ticket to Tier 2orlook up order status in Shopify.
Beyond the codebase: AI for support and IT teams
So, if the Claude Code GitHub integration is the answer for your engineering team, what’s the answer for your support and IT teams? This is where a purpose-built platform like eesel AI comes into play. It's designed from the ground up to solve the exact problems that the Claude integration doesn't.
eesel AI is a complementary tool built for business-facing automation. It connects to the platforms your support and IT teams use every day, like help desks, internal wikis, and chat tools. And unlike the complex, developer-led setup for the Claude integration, eesel AI is built to be simple and self-serve. You can get it up and running in minutes, not months, often without needing to bother your engineering team at all.
| Feature | Claude Code + GitHub | eesel AI for Support |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | Agentic software development | Customer & internal support automation |
| Setup Process | Developer-led (YAML, API keys) | Self-serve, no-code, one-click |
| Knowledge Sources | Code repository, CLAUDE.md | Helpdesk, Confluence, Google Docs, Slack |
| Typical Actions | Create pull requests, commit code | Triage tickets, draft replies, escalate |
| Ideal User | Software Developer | Support Manager, IT Lead, CX Ops |
Your next steps for AI-powered automation
Choosing the right AI tool is all about matching its capabilities to the job at hand.
For Your Engineering Team: The Claude Code GitHub Integration
Encourage them to check out the Claude Code GitHub integration. It’s a genuinely useful tool for making development workflows smoother, speeding up code reviews, and automating away the tedious parts of coding. When it comes to boosting developer productivity, it's a fantastic option.
For your support and IT teams
When your goal is to automate customer-facing support, resolve internal IT tickets instantly, or pull together knowledge from dozens of scattered sources, you need a platform built for that specific challenge. The right tool depends on the job, and for world-class support automation, you need a different approach.
Ready to automate your support workflows without the engineering headache? Start your eesel AI free trial and see how quickly you can reduce your ticket volume and make your team more efficient.
Frequently asked questions
The setup is designed for developers and requires a good understanding of GitHub. You'll need admin access to the repository to install the app, manage API keys in your repository's secrets, and create the [`claude.yml` configuration file](https://docs.anthropic.com/en/docs/claude-code/github-actions).
Yes, it's designed to do exactly that. The integration reads a file called `CLAUDE.md` in your repository, where you can define your project's [coding standards, architectural rules, and common practices](https://medium.com/google-cloud/accelerate-adk-development-with-claude-code-github-mcp-server-7a5052d481bc) to ensure its contributions are consistent with your team's work.
Not at all. It's best to think of it as an extremely fast junior developer that helps with initial reviews, catches common mistakes, and speeds up the process. It frees up your senior developers to focus on more complex architectural issues rather than replacing them.
Being specific and clear in your request is key. Instead of a vague prompt like "@claude fix this," provide a detailed command like "@claude fix the TypeError in the user dashboard." It's also helpful to iterate and provide feedback in follow-up comments if the first attempt isn't perfect.
No, this tool is not suitable for customer support. Its knowledge is limited to your codebase, and its actions are developer-focused, like creating pull requests. For [automating support](https://www.eesel.ai/blog/how-to-automate-your-customer-support-workflow-using-ai), you would need a purpose-built tool that can connect to help desks and wikis.
Share this post

Article by
Kenneth Pangan
Writer and marketer for over ten years, Kenneth Pangan splits his time between history, politics, and art with plenty of interruptions from his dogs demanding attention.