
If you’re digging into AI for customer service, you’ve probably seen the name Ada pop up. One of the key pieces for the tech-savvy crowd is the Ada End Users API, a tool designed to sync up user data and make chatbot chats feel more personal.
But let's clear one thing up first. The name "Ada" gets around. You might see it and think of the Ada programming language or even one of OpenAI's models. We're not talking about those. This guide is all about the API from Ada.cx, the AI customer service company.
We’ll walk through what their End Users API actually does, a tool designed to sync up user data and make chatbot chats feel more personal.
What is the Ada End Users API?
Think of the Ada End Users API as a special connection that lets your other business software (like your CRM or internal database) talk directly to your Ada chatbot. It’s a tool built for developers to share information about your users in real time.
The whole point is to make conversations less robotic. By syncing details like a customer's name, their purchase history, or what subscription plan they're on, your Ada chatbot can give specific, helpful answers instead of generic ones.
With the API, your developers can:
-
Create and update user profiles: Pull in customer details from other systems and feed them to Ada.
-
Manage custom data: Store unique bits of info for each user, like their membership tier or the date of their last order.
-
Use webhooks: Get automatic pings whenever a user profile is made or changed.
In short, it’s a technical tool to give your AI agent the context it needs to know who it’s talking to.
A look at the features of the Ada End Users API
The Ada End Users API is built on standard web technologies that most developers are familiar with, using JSON to move data back and forth. This is great for engineers, but it does mean you need technical folks to set it up and keep it running. Let's break down the main parts.
Managing user profiles and custom data
The heart of the API is the User Profile. It's a collection of information about a single user. Ada creates some of this automatically, but the real power comes from the custom data you can add. You can store things like "plan_type: "premium"" or "last_order_date: "2024-10-26"". This information can then be used to create rules inside Ada that change how the chatbot responds to different people.
Webhook support for instant updates
Ada also supports webhooks for two key events: when a new user starts a chat and when an existing user's profile gets updated. This means Ada can send an alert to another system you own whenever these things happen. It’s a good way to keep all your systems in sync, but it does require someone to build and manage a service that listens for these alerts.
The developer-first design
Using the API involves handling authentication with API keys, keeping track of different API versions, and writing code to make it all work. While it gives you a lot of control, this setup means your engineering team is on the hook for the initial setup, any future tweaks, and general maintenance.
A more modern alternative: While APIs give you control, they aren't the only way to get deep integrations. Modern platforms like eesel AI achieve the same goal with simple one-click integrations. Instead of asking your developers to build and maintain a data pipeline, you can just connect your help desk (like Zendesk or Freshdesk) and other knowledge sources directly. eesel AI learns from your past tickets and documents automatically, giving it all the context it needs without any tricky API projects.
Common uses of the Ada End Users API
So, why would a team go through the trouble of setting this up? Usually, it's to solve a few common problems in customer support.
Making customer chats more personal
Personalization is the biggest reason. Let's say you run an online store. With the API, the chatbot could grab a customer's latest order ID from your system and show its status right in the chat. That’s a world away from the classic "Please find your 16-digit order number and type it below" experience.
Syncing data from other systems
Most of the time, your key customer data lives in a CRM like Salesforce or a custom-built database. The API acts as the bridge to get that information into Ada, making sure the AI agent has the same facts as your human agents.
Ada End Users API technical hurdles: Rate limits and setup
Getting the API running isn't exactly a walk in the park. According to Ada's own documentation, the API has pretty strict limits on how often you can make requests (for example, 300 requests per minute for user data). For businesses with a lot of customer chats, you’ll need to plan carefully to avoid hitting those limits and causing interruptions.
On top of that, testing an API integration is a whole project in itself. You need a separate testing environment and developer time to make sure data is flowing correctly. And every time you want to add a new piece of data for personalization, it’s back to the engineering team for another cycle of development.
Limitations of the Ada End Users API approach and a more flexible alternative
While the Ada End Users API gives you a way to add context to chats, its reliance on developers and its siloed nature can create real problems for busy support teams.
The engineering bottleneck
Any change, update, or new data source requires a developer. This creates a bottleneck that slows your support team down. Want to personalize conversations based on a new customer attribute? You’ll have to file a ticket with the engineering team and wait your turn. This is a far cry from the self-serve tools that modern teams expect.
A closed system vs. connected knowledge
The API is built to pull data into Ada's world. But what about all the knowledge that already exists elsewhere? Your team's expertise is probably spread across Google Docs, Confluence, Notion, and other internal documents. An API-first model doesn't solve the bigger problem of bringing all that scattered knowledge together.
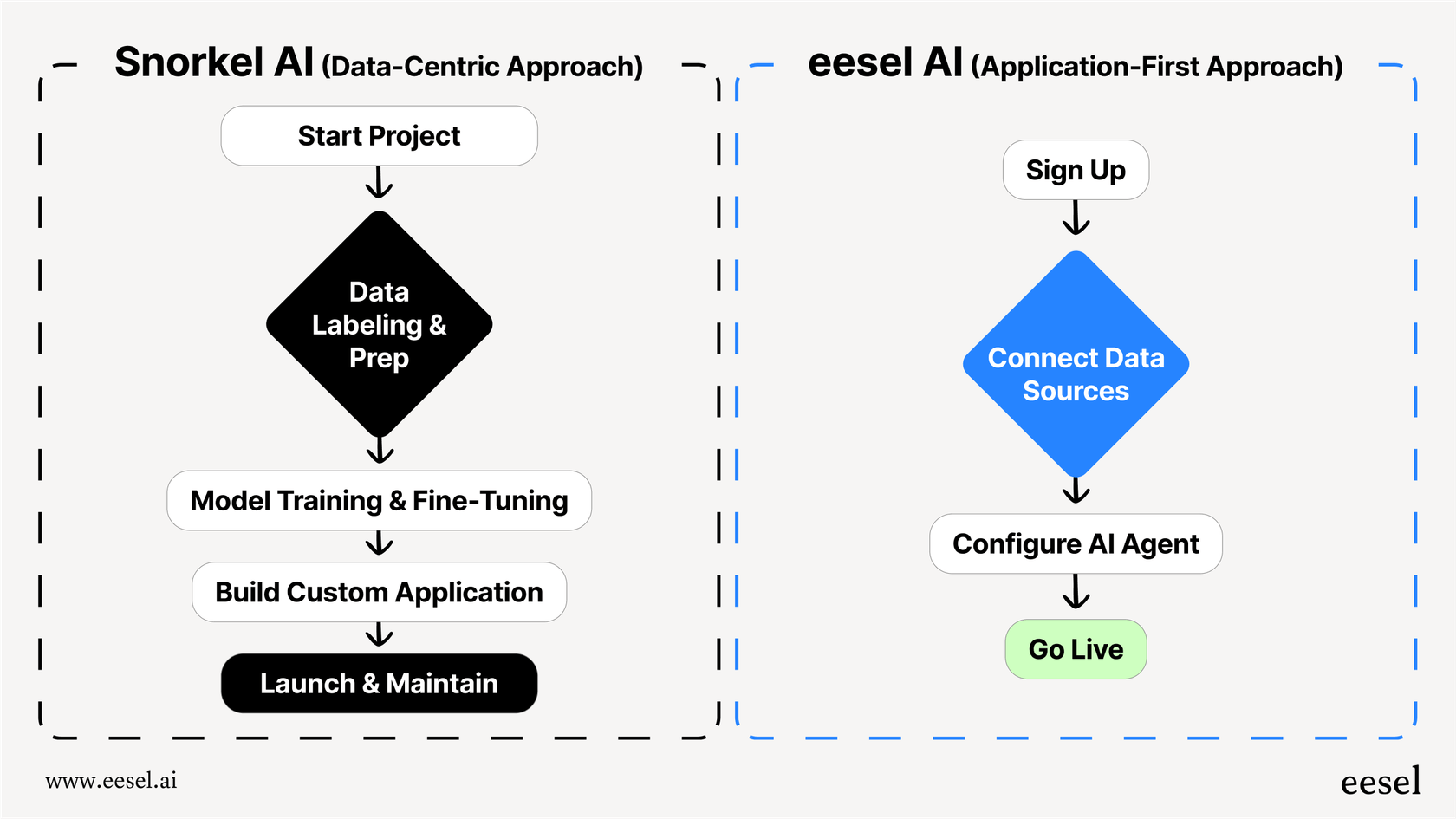
The eesel AI alternative: Connect everything instantly
This is where a platform like eesel AI takes a completely different path. Instead of making you push data into a closed system with an API, eesel AI connects to all the tools and knowledge sources you already use with one-click integrations.
Here’s how it works:
-
It learns from your past tickets: From day one, it analyzes your historical support conversations to understand your common issues and your brand's voice.
-
It connects to all your knowledge: You can seamlessly integrate your help center articles, company wikis, and even internal chat history from tools like Slack.
-
It works inside your existing help desk: eesel AI fits right into your current workflow, so you don't have to switch to a whole new platform.
This approach gives you deep personalization and accurate answers without writing a single line of code. You can get up and running in minutes, not months.
Ada pricing
Trying to find Ada's pricing on their website is tough because it isn't publicly listed. You have to fill out a form and talk to their sales team to get a quote. This can make it hard to budget, since the final price might change based on your support volume, the features you need, and how the sales conversation goes.
In contrast, eesel AI has transparent and predictable pricing based on clear feature tiers and a set number of AI interactions. There are no sneaky per-resolution fees, so your costs won't suddenly jump during your busiest months.
| Plan | Effective /mo Annual | AI Interactions/mo | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Team | $239 | Up to 1,000 | Train on website/docs; AI Copilot; Slack integration. |
| Business | $639 | Up to 3,000 | Everything in Team + train on past tickets; AI Actions; bulk simulation. |
| Custom | Contact Sales | Unlimited | Advanced actions; multi-agent orchestration; custom integrations. |
Moving beyond rigid APIs with an integrated AI platform
The Ada End Users API is a solid tool for development teams who want to build highly customized chatbot experiences from the ground up. However, it comes with the heavy baggage of developer dependency, a complex setup, and an approach that boxes your knowledge into one place.
For most support teams, a faster and more effective solution is a platform that connects to all your existing knowledge and tools without needing a single line of code. eesel AI lets you set up a powerful AI agent that learns from your entire company's brain in minutes.
Ready to see how a truly connected AI platform can change your customer support? You can try eesel AI for free.
Frequently asked questions
The Ada End Users API acts as a bridge, allowing your existing business software (like CRM) to share user data directly with your Ada chatbot. Its primary purpose is to provide the chatbot with real-time context about individual users to make conversations more personal and relevant.
By syncing customer details such as purchase history, subscription plans, or specific order IDs, the Ada End Users API enables the chatbot to offer highly specific and personalized responses. This moves beyond generic answers to provide more helpful and tailored interactions.
Implementing the Ada End Users API requires developers familiar with standard web technologies, JSON, and API authentication. The setup, ongoing maintenance, and any new data integrations all rely on your engineering team.
Yes, the Ada End Users API is specifically designed to facilitate this connection. It allows developers to pull key customer data from systems like Salesforce or custom databases directly into Ada, ensuring the AI agent has consistent information.
A major drawback is the reliance on developers for every change or new integration, creating potential bottlenecks. It also operates as a somewhat closed system, requiring data to be pushed into Ada rather than seamlessly connecting to all existing knowledge sources.
The Ada End Users API supports webhooks for events like new user chats or user profile updates. This allows Ada to send alerts to other systems, helping to keep all your platforms synchronized with the latest user information.
Share this post

Article by
Stevia Putri
Stevia Putri is a marketing generalist at eesel AI, where she helps turn powerful AI tools into stories that resonate. She’s driven by curiosity, clarity, and the human side of technology.







